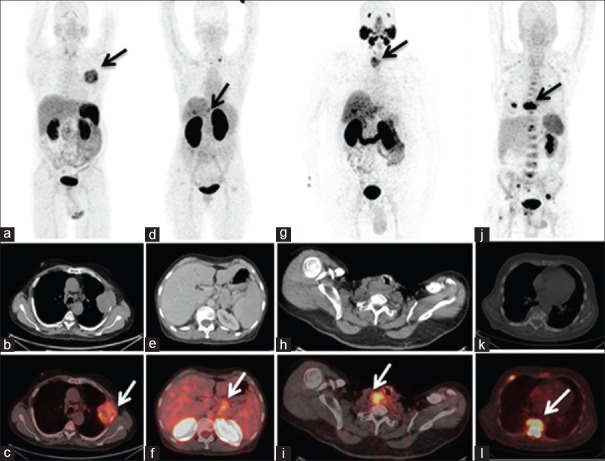
Figure 1.
(a-c) Ga-68-DOTA-RGD2 positron emission tomography images, maximum intensity projection (a) acquired of a 62-year-old male patient with squamous cell lung carcinoma showing intense uptake of radiotracer in the left hemi-thorax corresponding to a heterogeneously enhancing pleural based soft-tissue mass lesion (SUVmax 7.8) on the transaxial computed tomography (b) and fused positron emission tomography-computed tomography (c) images in left lung with involvement of adjacent rib. (d-f) Ga-68-DOTA-Exendin-4 positron emission tomography images, maximum intensity projection (d) and transaxial computed tomography (e) and fused positron emission tomography-computed tomography (f) of a 57-year-old female patient with G1 neuroendocrine tumor of the pancreas showing uptake of radiotracer (SUVmax 5.8) in pancreatic tumor mass (arrow) with metastasis to liver and left supraclavicular lymph node. (g-i): Ga-68-HBED-CC-PSMA positron emission tomography images, maximum intensity projection (g), transaxial computed tomography (h) and fused positron emission tomography-computed tomography (i) of 58-year-old male patient with differentiated thyroid carcinoma posttotal thyroidectomy, showing intense tracer uptake in the right trachea-esophageal groove (SUVmax 11.2), representing local recurrence in the neck in a case of thyroglobulin elevated negative iodine scan. (j-l) Ga-68-CPCR4 trifluoroacetate positron emission tomography images, maximum intensity projection (j), transaxial computed tomography (k) and fused positron emission tomography-computed tomography (l) of a 63-year-old male patient diagnosed with multiple myeloma, showing abnormal foci of tracer uptake in multiple ribs, cervico dorso lumbar vertebra (D9 vertebra SUVmax 22.42), sternum and multiple sites in pelvis