Fig. 1.
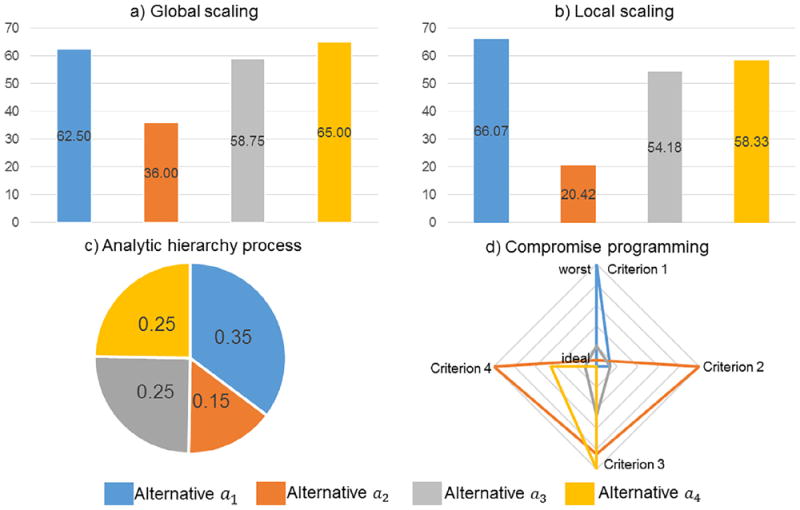
Benefit function values from the hypothetical multi-criteria problem using the global scaling (a), local scaling (b), and analytic hierarchy process (c) methods. Higher benefit function values correspond to more preferred alternatives. Distance function values using the compromise programming method (d). Performance values for each criterion range from “worst” = 1 to “ideal” = 0; alternatives closer to the ideal (lower distance function values) are preferred.
