Figure 3.
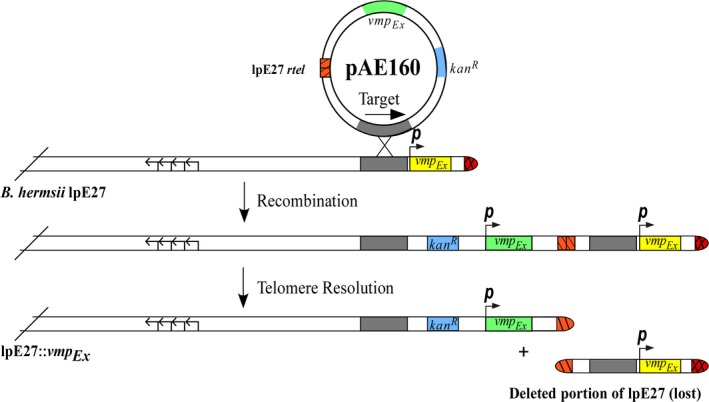
Generation of a functional in cis vmp Ex complementation mutant. In cis complementation of vmp Ex was achieved by a simultaneous deletion of the native locus and introduction of a cloned vmp Ex. The plasmid pAE160 possesses a target site for homologous recombination that lies just upstream of vmp Ex, a kanamycin resistance locus (kan R), a replicated telomere (rtel, orange stripes), and an introduced vmp Ex (shown in green). Following homologous recombination at the target sequence, the pAE160 plasmid is integrated into lpE27. Endogenous ResT acts upon the introduced rtel and all downstream sequence is deleted, including the native vmp Ex (yellow). The resultant mutant, Bh::Comp, now possesses an lpE27 plasmid with a vmp Ex and kan R. The direction and promoters of the vmp Ex loci are depicted as p, with arrows; four arrows depict the location of genes required for autonomous replication of lpE27
