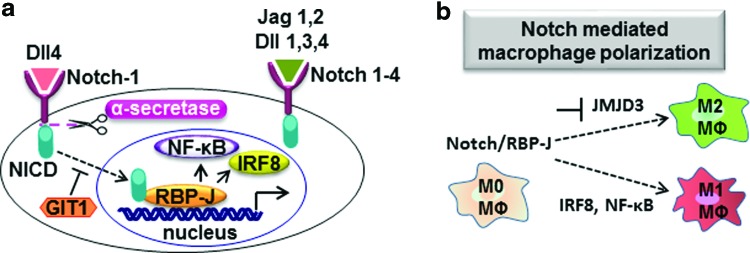
FIG. 5.
(a) The role of Notch signaling in macrophage polarization. Notch signaling promotes M1 macrophage polarization by synthesizing IRF8 and NF-κB and inhibits M2 macrophage polarization by downregulating JMJD3. (b) The Notch signaling pathway. The Notch ligands (Dll1, Dll3, and Dll4 and Jag1 and Jag2) bind to the Notch receptors (Notch 1–4). Upon ligand binding to the Notch receptor, proteolytic cleavage takes place (via α-secretase) in Notch receptor, resulting in the release of NICD. The NICD translocates to the nucleus and binds to RBP-J, resulting in the release of IRF8 and NF-κB. The GIT1 inhibits the Notch1-Dll4 mediated signaling. Dll, delta like; GIT1, G protein-coupled receptor-kinase interacting protein-1; IRF8, interferon regulatory factor 8; Jag, Jagged; JMJD3, Jumonji domain-containing 3; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa light chain enhancer of activated B cells; NICD, Notch intracellular domain; RBP-J, recombining binding protein suppressor of hairless. To see this illustration in color, the reader is referred to the web version of this article at www.liebertpub.com/ars