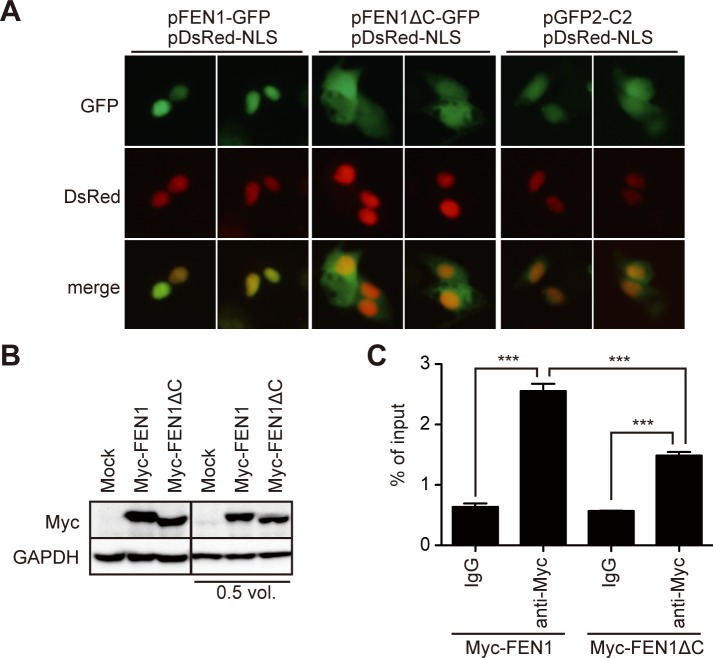
Fig 5. Deletion of the C-terminus disrupts the nuclear localization and reduces HBV DNA association of FEN1 protein.
(A) Expression vectors of FEN1-GFP, FEN1ΔC-GFP, or mock vector (pcDNA4/TO) were transfected into Hep38.7-Tet cells. The nucleus was visualized by co-transfection of the nuclear localization signal (NLS)-tagged DsRed vector. (B–C) Myc-FEN1 or Myc-FEN1ΔC vector was transfected into Hep38.7-Tet cells. (B) Myc-tagged protein expression (before cross linkage) shown by Western blot. Two blots with different protein loadings are shown. (C) Myc-FEN1-transfected Hep38.7-Tet cells were cross-linked, and the lysates were immunoprecipitated with either control IgG or anti-Myc antibody. The immunoprecipitants were subjected to qPCR analysis using a primer pair to detect the core region of HBV. Each result represents the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences; ***P < 0.001.