Figure 2. Glycopeptide antibiotics inhibit both PG transglycosylation and WTA biosynthesis in S. aureus.
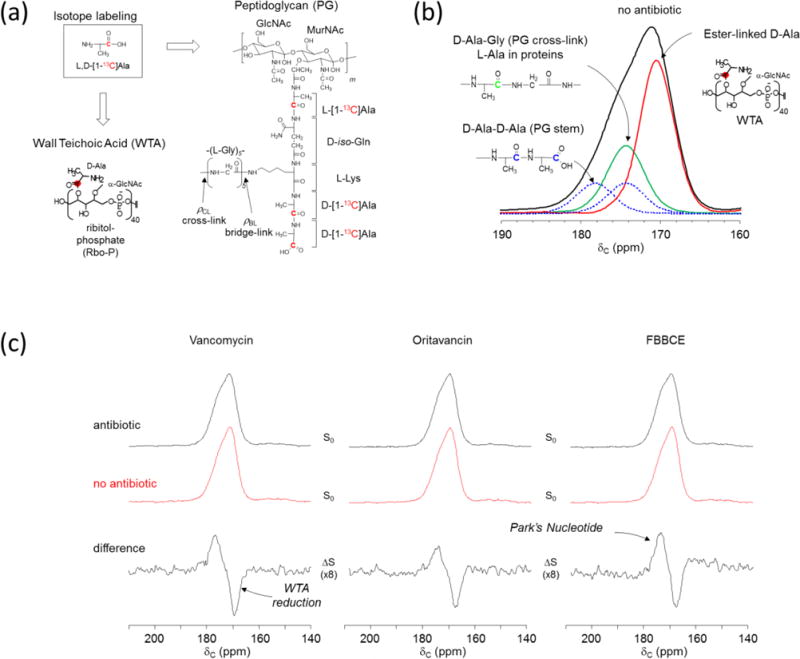
a, PG and WTA labeling by L,D-[1-13C]Ala in S. aureus. b, Deconvolution of 13C-CPMAS spectrum of intact whole cells of S. aureus with D-alanyl carboxyls at 178 ppm (blue), D-alanyl peptide carbonyls at 174 ppm (green), and ester carbonyls of WTA at 171 ppm (red). c, 13C-CPMAS spectrum of untreated S. aureus (middle, red) is subtracted from the spectrum of antibiotic treated whole cells (top, red). The difference spectra (bottom) show all antibiotic-treated S. aureus have a negative 171 ppm peak which corresponds to decreased ester-linked D-Ala incorporation to WTA. Park’s nucleotide accumulation (positive 178 ppm peak) is observed for all glycopeptide-treated S. aureus.
