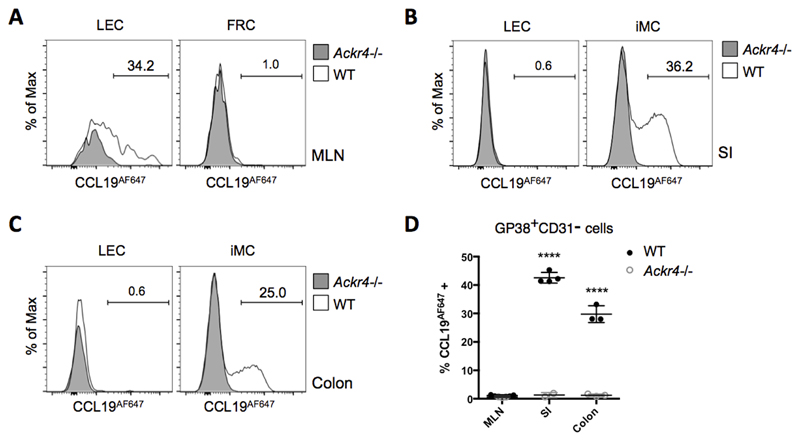
Figure 2. ACKR4 is expressed as a functional protein on a subset of iMCs and MLN LECs.
Single cell suspensions prepared from WT and Ackr4-deficient (Ackr4-/-) mice (Ackr4tm1.1Rjbn) were incubated in medium containing CCL19AF647 for 1h at 37°C, then labelled with fluorescent Abs, and analysed by flow cytometry. Stromal cell subsets were identified from among live, single, CD45-Ter119- cells. (A-C) Representative overlaid histogram plots showing uptake of CCL19AF647 by lymphatic endothelial cells (LEC) and GP38+CD31- cells (i.e. fibroblast reticular cells (FRC) or intestinal mesenchymal cells (iMC)) from (A) MLN (B) small intestine (SI), and (C) colon of WT and Ackr4-/- mice. The numbers on the plots indicate the percentage of CCL19AF647-positive cells in the WT samples. (D) Mean percentage of CCL19AF647-positive cells (±1SD) in the GP38+CD31- population in the MLN, SI and colon of WT and Ackr4-/- mice (n=3/4 per group). Data are representative of two individual experiments. ****p<0.0001, unpaired Student’s t test, comparing data from the same tissue from WT vs Ackr4-/- mice.