Fig 1.
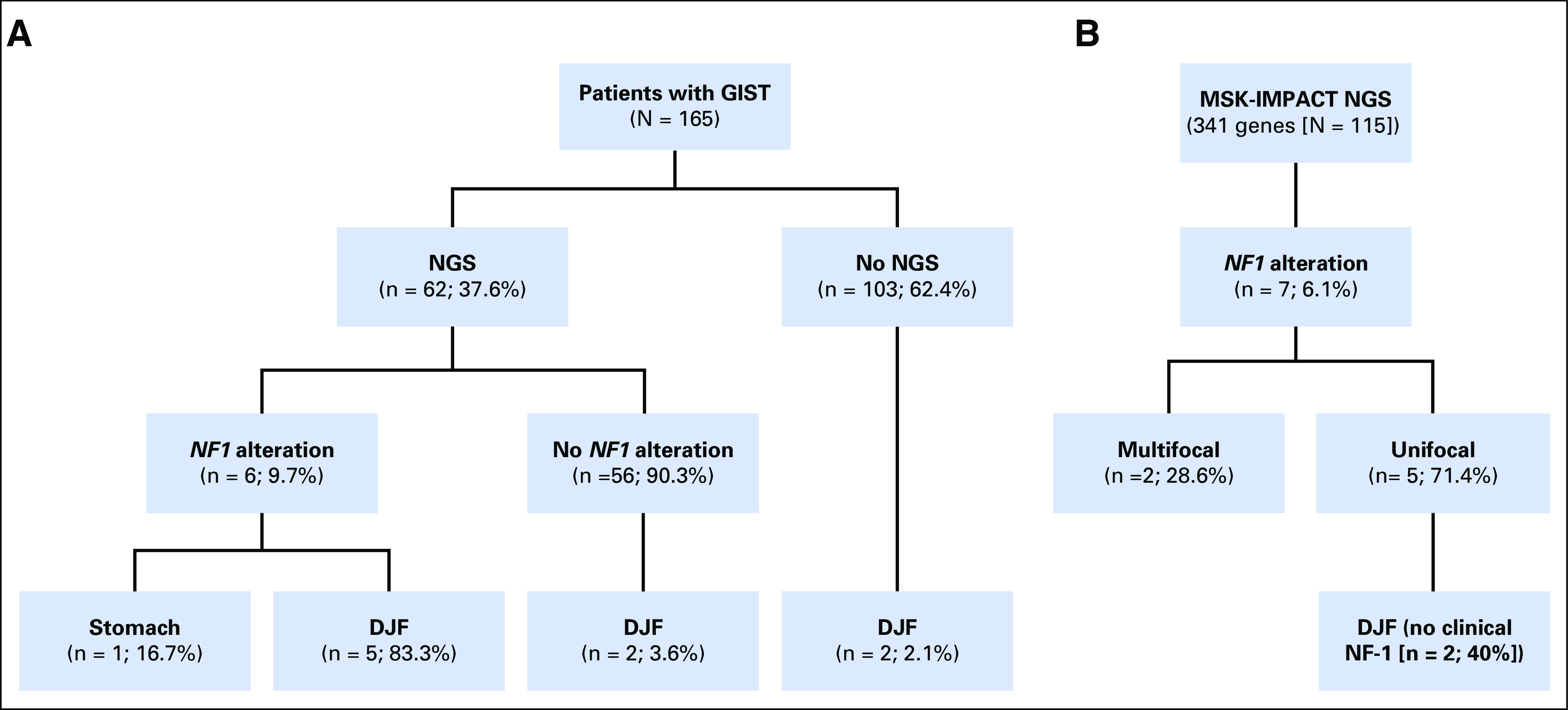
Schematic of patients with NF1-altered GI stromal tumors (GISTs). (A) From a total of 165 patients (University of California, San Diego [UCSD]) with pathologically confirmed GISTs, 62 had available next generation sequencing (NGS). Of these 62 patients, six had NF1 genomic alterations. (Seventeen tumors in the UCSD NGS cohort, including two duodenal-jejunal flexure [DJF] GISTs, were previously included in an earlier study of pooled international data that aimed to identify novel deleterious genomic alterations in GISTs that lack canonical driver mutations.7) (B) From a validation cohort (Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center) of 115 patients with pathologically confirmed GISTs and available NGS, seven had NF1 genomic alterations. Five of these tumors were unifocal, and from two of these five, unifocal NF1-mutated GISTs arose from the DJF. MSK-IMPACT, Memorial Sloan Kettering-Integrated Mutation Profiling of Actionable Cancer Targets.
