FIG 1.
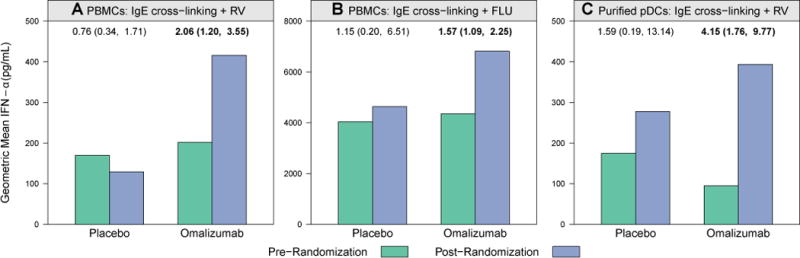
Enhanced PMBC and pDC IFN-α responses after omalizumab. PBMC and pDC IFN-α responses to rhinovirus (RV) and influenza virus (FLU) significantly increased during the intervention phase of the study in the omalizumab group. Bars represent geometric mean IFN-α concentrations (in picograms per milliliter) measured in supernatants. Ratio of geometric means comparing postintervention versus preintervention values within each group are annotated above the bars, along with associated 95% CIs. Boldface indicates a P value of less than .05, as determined by using the paired t test. A, A 2.06-fold increase in PBMC IFN-α response to rhinovirus plus IgE cross-linking (P = .01). B, A 1.57-fold increase in PBMC IFN-α response to influenza virus plus IgE cross-linking (P = .02). C, A 4.15-fold increase in pDC IFN-α response to rhinovirus plus IgE cross-linking (P = .003) was observed between prerandomization (green bars) and postrandomization (blue bars) values in the omalizumab group.
