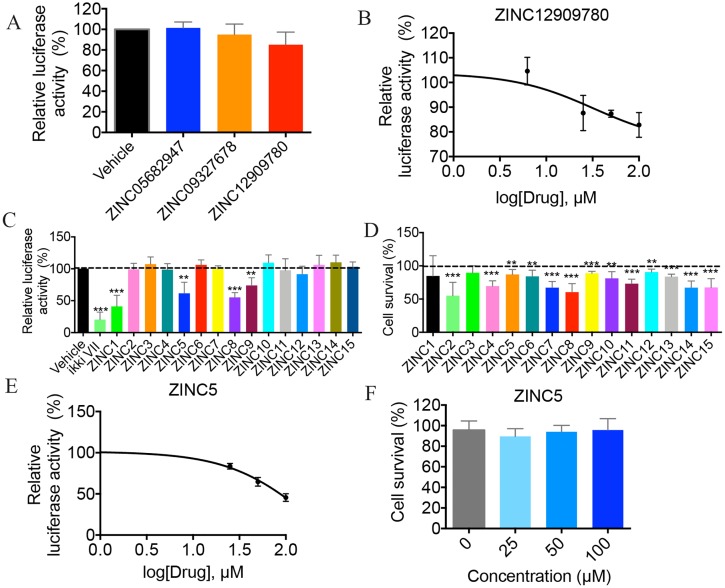
Fig 2. Identification of small molecules inhibiting TNF-α-induced NF-κB activation.
(A) HEK293 cells stably expressing NF-κB luciferase reporter were pretreated with indicated small molecules at 100 μM for 30 min, followed by stimulation with TNF-α (10 ng/ml) for 3 h. Luciferase activity was normalized to untreated stimulated control cells. Data show the mean values of 2 independent experiments +/− SD. (B) The dose-dependent response of ZINC12909780 was tested by NF-κB luciferase assay in HEK293 cells. Three independent experiments were performed, and data shown represent mean +/− SD. (C) HEK293 cells were treated with derivatives of ZINC12909780 at 100 μM, and NF-κB luciferase assay was performed to screen for small molecules with greater NF-κB inhibitory effect. Data show the pooled results of 5 independent experiments and are the mean +/− SD. (D) HEK293 cells were cultured in the presence of 100 μM of indicated derivatives for 24 h, and cell survival was determined by MTT assay. Cell viability was calculated by normalizing to untreated cells. (E) Dose-dependent inhibitory effects were determined for ZINC5 at 0, 25, 50, and 100 μM by using NF-κB luciferase assay. (F) HEK293 were cultivated in the presence of ZINC5 at listed concentrations for 24 h, and cell survival was assessed by MTT assay. Data represent the mean +/− SD from 4–5 independent experiments. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. Underlying data can be found in S1 Data. HEK293, human embryonic kidney 293 cells; MTT, 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-dephenyltetrazolium bromide colormetric assay for assessing cell metabolic activity; NF-κB, nuclear factor κB; TNF-α; tumor necrosis factor α; SD, standard deviation.