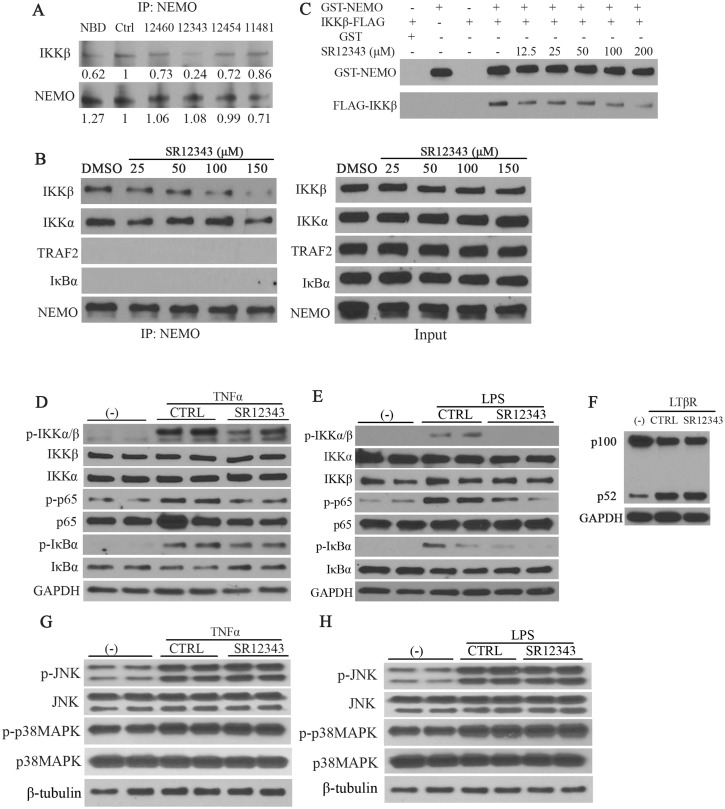
Fig 5. NBD mimetics selectively inhibit canonical NF-κB signaling by targeting the association of NEMO with IKKβ.
(A) Co-IP analysis detecting the IKKβ/NEMO interaction. Raw 264.7 cells were pretreated with the indicated drugs, DMSO, 8K-NBD peptide (400 μM), SR12460 (100 μM), SR12343 (100 μM), SR12454 (100 μM), and SR11481 (100 μM) for 30 min, and the cells were then harvested for Co-IP. NEMO was probed as a loading control. (B) Raw 264.7 cells pretreated with SR12343 at indicated concentrations (0, 25, 50, 100, and 150 μM) for 30 min were subjected to Co-IP assay. NEMO-binding products were then analyzed for levels of IKKβ, IKKα, TRAF2, and IκBα (negative control), and levels of NEMO were used as a loading control (left panel). Right panel shows levels of proteins in input controls (10% of cell extract used for Co-IP). (C) GST-NEMO (15 nM), preincubated with inhibitors at indicated concentrations, was incubated with IKKβ-FLAG (15 nM) for 30 min at 30 °C and isolated using Glutathione argarose. The levels of IKKβ-FLAG binding to GST-NEMO were determined by western blot analysis with GST-NEMO used as a loading control. (D, E) Raw 264.7 cells pretreated with vehicle control or SR12343 (150 μM) for 30 min were stimulated with or without 10 ng/ml TNF-α (D) or 1 μg/ml LPS (E) for 10 min. Cell lysates were analyzed for activity of the IKK/NF-κB signaling pathway including activation of IKK complex, IκBα, and p65. GAPDH was used as a loading control. (F) Raw 264.7 cells were incubated with vehicle control or SR12343 (100 μM) for 30 min, followed by stimulation with or without anti-LTβR for 8 h. Cell lysates were harvested and analyzed for activation of noncanonical NF-κB signaling, the processing of p100 to p52. (G, H) Analysis of the effects of SR12343 (150 μM) on phosphorylation of JNK and p38MAPK in response to TNF-α (G) or LPS (H), using the same cell lysate being used in panels D and E. Co-IP, co-immunoprecipitation; GST, glutathione S-transferase; IKK, IκB kinase; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; LTβR, lymphotoxin β receptor; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; NBD, NEMO-binding domain; NEMO, NF-κB essential modulator; NF-κB, nuclear factor κB; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; TRAF2, TNF receptor-associated factor 2.