Figure 1.
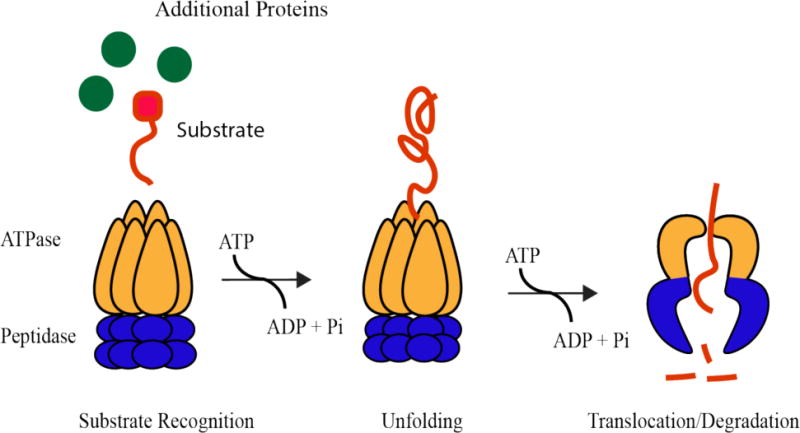
Energy-dependent proteases are composed of an ATP-hydrolysis active unfoldase domain and a chambered peptidase domain. Through successive rounds of ATP hydrolysis, a specific substrate protein is selected by the protease, unfolded by the ATPase domain, and translocated through a central pore to the peptidase chamber where it is degraded.
