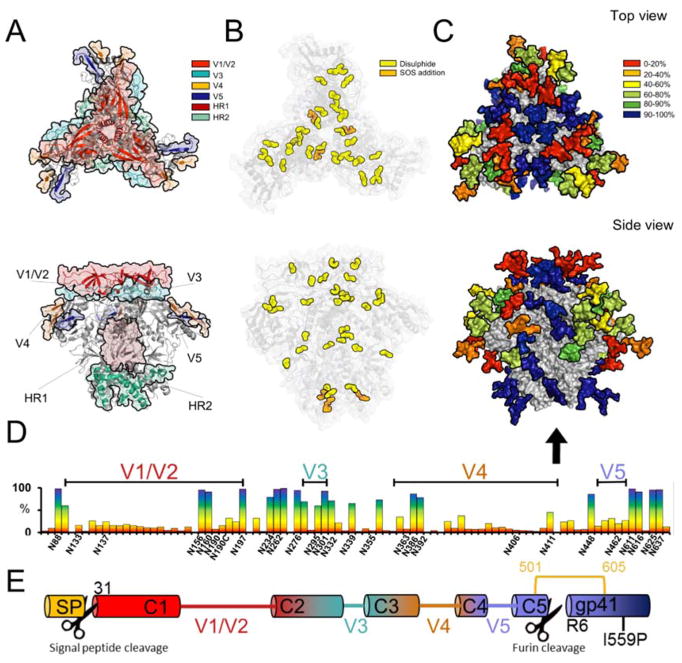
Figure 1. Representation of the post-translational modifications of BG505 clade A envelope glycoprotein.
Models were generated using the cryo-EM structure of BG505 SOSIP.664 PDB ID:5ACO [12]. A) 3D representation of the variable loops on gp120 and the heptad repeats of gp41. B) Canonical disulphide bonds found in BG505[36] with the additional stabilizing disulphide bond found in BG505 SOSIP.664 shown in orange. C) Conservation map of the glycans of BG505 SOSIP.664. The glycans were coloured according to their conservation across 4000 Env strains Huang et al.[44]. BG505 crystal structure with N-linked glycans modelled by Behrens et al.[52] D) The frequency of potential N-linked glycan sites across the Env sequence with the PNGs found in BG505 SOSIP.664 labelled on the X axis. E) Schematic showing the locations of proteolytic cleavage for the signal peptide and the furin cleavage site.