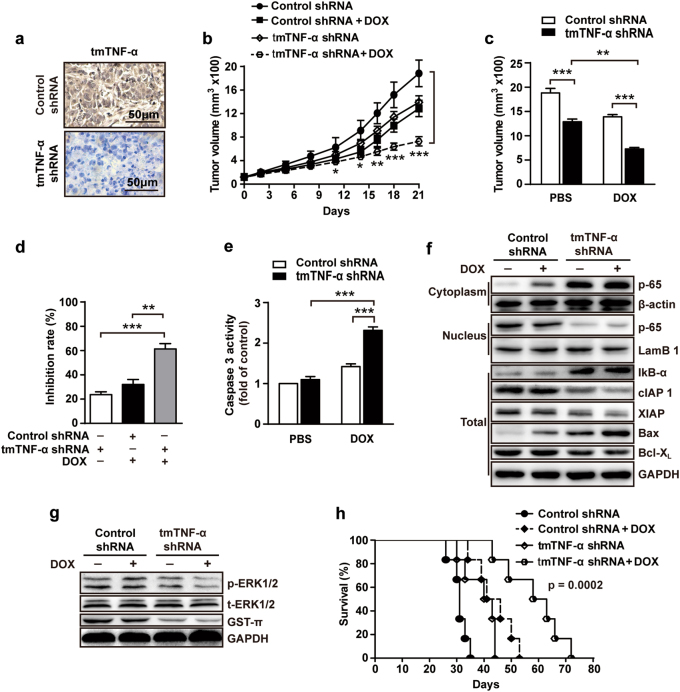
Fig. 6.
Knockdown of tmTNF-α expression enhances the therapeutic efficacy of DOX in vivo. 1 × 106 MDA-MB-231 cells transfected with control or tmTNF-α shRNA were injected into mammary fat pad of nude mice. When tumors reached 100 mm3, the mice were treated intraperitoneally with DOX (4 mg/kg) or PBS, once a week for three weeks (n = 6 each group). a Representative images of tmTNF-α expression in tumor tissue section detected by IHC. b Growth curves of tumors after tumor cell inoculation. c Tumor sizes at the end point (day 21) of experiments. d Inhibition rate of tumor growth. e Caspase 3 activity in tumor tissues at day 21. f Immunoblotting of levels of IκB-а, cIAP1, cIAP2, XIAP, BAX, and Bcl-XL in total protein and translocation of NF-κB p65 from cytoplasmic fraction to nuclear fraction of tumor tissues. g Immunoblotting of levels of phosphorylation of ERK and GST-π in tumor tissues. h Kaplan–Meier survival curves of mice after tumor cell inoculation (n = 6). Data are represented as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001