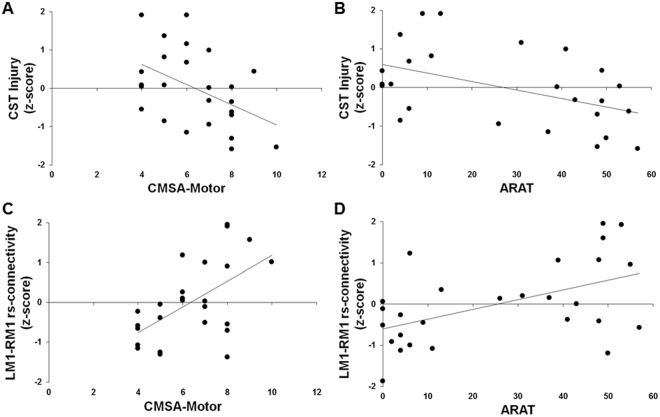
Figure 3.
Relationship between structural and functional biomarkers and motor outcome. Scatterplots of biomarkers and motor assessment scores. Injury to the corticospinal tract (CST Injury) accounts for 23% variance in (A) the Chedoke-McMaster Stroke Assessment: Impairment Inventory Total Motor Impairment (CMSA-Motor) score, and 24% variance in (B) the Action Research Arm Test (ARAT) score. Resting state connectivity between left and right primary motor cortex (LM1-RM1 rs-connectivity) accounts for 34% variance in (C) the CMSA-Motor score, and 22% variance in (D) the ARAT score.