Fig. 10.
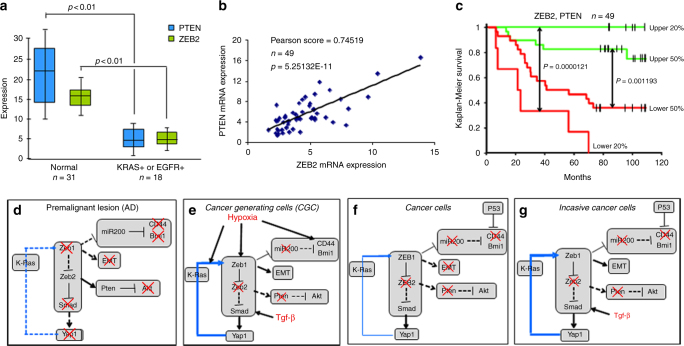
A ZEB2, PTEN predicts survival in human lung AC, and model of precancerous lesion transition to lung cancer. a Box plot showing expression of ZEB2 and PTEN mRNAs in human lung AC. The top of the box is the 75 percentile, whereas the bottom is the 25 percentile. The bar indicates the median and whiskers the highest and lowest values. K-Ras+ and EGFR+ indicate mutations confirmed by sequencing, and “Normal” indicates adjacent uninvolved lung tissue. b Pearson plot demonstrating a linear correlation between ZEB2 and PTEN mRNA levels in tumors in a. c Survival curves showing a ZEB2, PTEN expression signature predicts survival in human lung AC. d Precancerous adenoma (AD) lesions. K-Ras mutation triggers cell proliferation leading to the outgrowth of lung epithelial cells into AAH and AD. Red “X” indicates a block. The blue line running through K-Ras shows that, when activated, Yap1 can bypass the ongoing requirement for K-Ras mutation in tumors40–42. Dashed lines indicate inactivated pathways, whereas solid lines show activated pathways. The font size of Zeb1, Smad, and Yap1 depict relative level of expression or activation. e Cancer-generating cells (CGC). Hypoxia and Tgf-β1 accumulation in the interior of expanding AD triggers formation of CGC. f Cancer cells. As cancer cells form from CGC and migrate away from Tgf-β1-rich hypoxic clusters, Zeb1 expression diminishes. This lower level of Zeb1 is sufficient to maintain repression of miR-200 and induction of Bmi1, and repression of Zeb2 leading to repression of Pten and nuclear Yap1. But, this lower level of Zeb1 is not sufficient to maintain EMT. And, CD44 is low in the cancer cells, consistent with its dominant repression by p53. g Invasive cancer. As cancer cells encounter Tgf-β1-rich airways, Zeb1 is induced and the cells again undergo EMT. This depicts plastic EMT in cancer cells linked to invasion. But, this induction of Zeb1 in invading cancer cells does not lead to re-expression of CD44 or asymmetry of heterochromatin, Numb, and transcription factors in poles of dividing cells, as with CGC