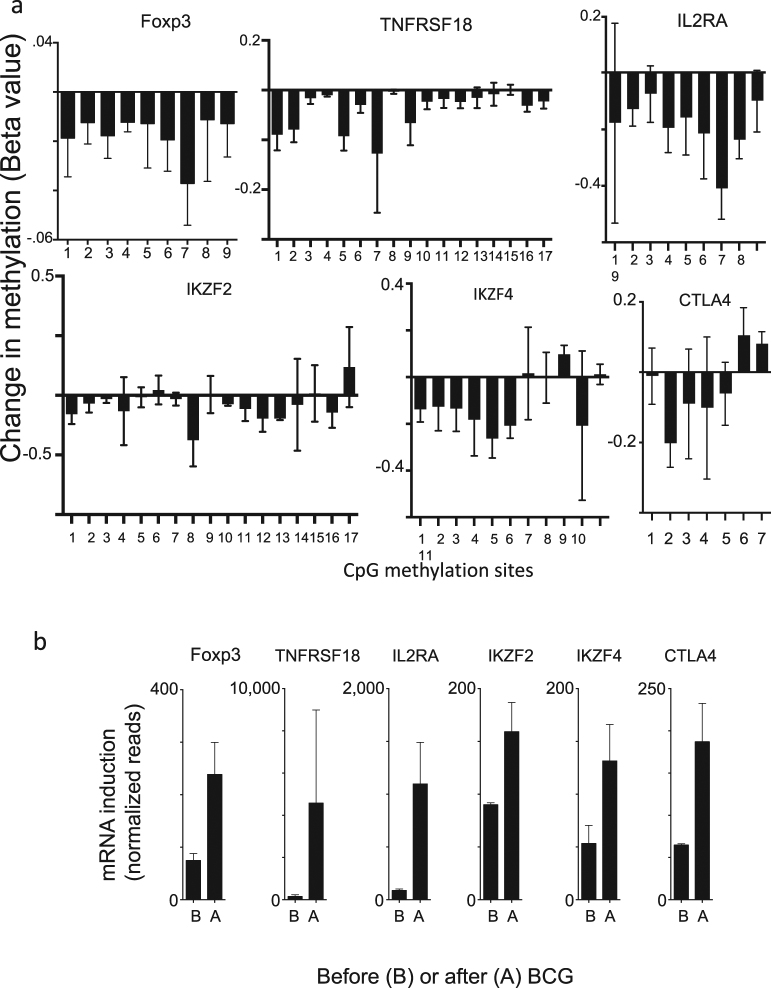
Fig. 2.
BCG treatment reduces DNA methylation and upregulates expression of Treg signature genes. a CD4 T cells were isolated from T1D patients before and after BCG treatment (n = 3 subjects; Supplementary Table S1a). DNA was isolated, bisulfite converted and analyzed on the Illumina Infinium HumanMethylation 450 BeadChip array. The data shows that after BCG treatment all six Treg signature genes are demethylated at multiple CpG methylation sites. For a table of the CpG sites used please see Supplementary Table S3. This data compares the methylation state in BCG-treated diabetics 8 weeks after administration of the two BCG vaccines against their pre-treatment baseline. For the Foxp3 gene, all nine methylation sites on the BeadChip were significantly demethylated after BCG treatment (FDR adjusted p = 0.004). For the TNFRSF18 gene (also known as GITR receptor), 16 out of 17 methylation sites on the Beadchip were demethylated after BCG and one site was unchanged (FDR adjusted p = 0.0008). For the IL2RA gene all 9 methylation sites on the chip showed decreases in methylation after BCG treatment (FDR adjusted p = 0.003). For the IKZF2 gene, also known as IKAROS family zinc finger 2 (Helios), there are 17 sites on the chip. After BCG treatment, 13 of those sites were de-methylated, 1 site showed augmented methylation, and 3 sites were unchanged. Overall, demethylation of the IKZF2 sites after BCG treatment was not statistically significant with FDR adjusted p = 0.106. For the IKZF4 gene, also known as IKAROS family zinc finger 4 (Eos), there are 11 methylation sites represented on the chip. After BCG treatment, 8 sites were de-methylated and 3 sites showed augmented methylation. Overall the IKZF4 sites were significantly demethylated after BCG treatment (FDR adjusted p = 0.038). For the CTLA4 gene, there were 7 sites represented on the chip. After BCG treatment, 5 sites were demethylated and 2 sites showed increases in methylation. Overall there was no significant difference in CTLA4 sites before and after BCG treatment (FDR adjusted p = 0.509). This data is from 3 subjects receiving BCG therapy (Supplementary Table S1a). b RNA was isolated from PBLs of three T1D before and after in vitro culture with BCG for 48 h and analyzed using RNAseq or transcription profiling. BCG treatment caused a sharp increase in the amount of mRNA as expressed by the number of RNAseq reads for each of the six Treg signature genes that promote Treg function and correlated with the de-methylation patterns