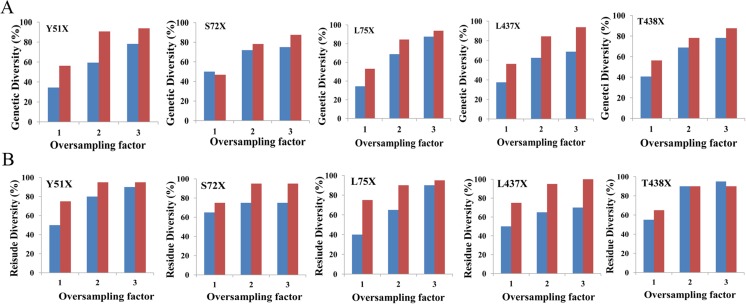
Fig. 2.
Genetic diversity (a) and residue diversity (b) for each NNK-based SSM library for both one-step PCR (blue bar) and two-step (red bar) PCR methods based on different oversampling factors. Genetic diversity is defined by the ratio of the number of codons obtained after sequencing to the number of theoretically possible codons expected (32) expressed in percentage; residue diversity is defined by the ratio of the number of residues obtained after sequencing to the number of theoretically possible residues expected (20) expressed in percentage