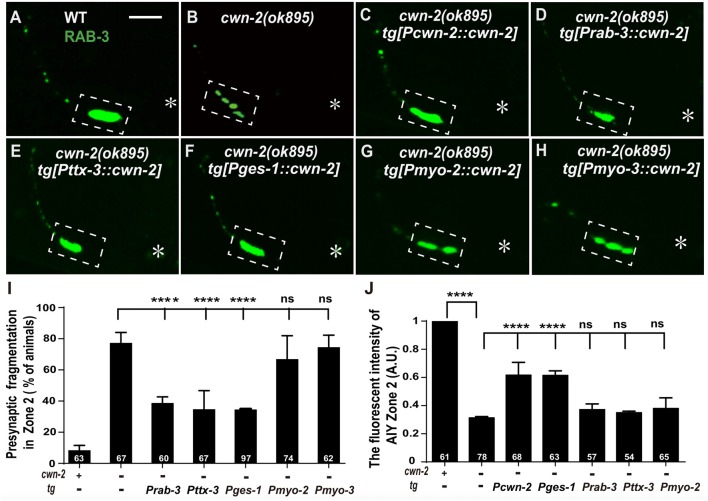
Figure 4.
cwn-2 acts in nervous system and intestine to regulate AIY synaptic clustering. (A–H) Confocal micrographs of the AIY presynaptic pattern of GFP::RAB-3. Presynaptic marker GFP::RAB-3 forms a large continuous cluster at AIY Zone 2 in wild type animals (A), and the cluster is fragmented in cwn-2(ok895) mutants (B). This Zone 2 fragmentation in cwn-2(ok895) is rescued by driving expression of cwn-2 with its own promoter (C), pan-neuronal rab-3 promoter (D), AIY-specific ttx-3 promoter (E) or intestinal-specific ges-1 promoter (F), but not with pharyngeal-specific myo-2 promoter (G) or body wall muscle-specific myo-3 promoter (H). Dashed boxes highlight AIY zone 2 and asterisks indicate the position of AIY soma. The scale bar represents 10 μm. (I,J) Quantification of the GFP::RAB-3 fragmentation (I) or fluorescence intensity (J) in AIY Zone 2. The Zone 2 fragmentation phenotype is rescued by expressing cwn-2 either in the nerve system (with pan-neuronal rab-3 promoter or with AIY-specific ttx-3 promoter) or in the intestine (with ges-1 promoter), while the GFP::RAB-3 intensity can only be rescued by expressing cwn-2 in the intestine, not in the nerve system. Data for each genotype are averaged from at least three biological replicates. Transgenic data are averaged from at least two independent lines. ns: not significance, ****p < 0.0001, analyzed by one-way ANOVA Dunnett’s test. Error bars represent 95% confidence interval.