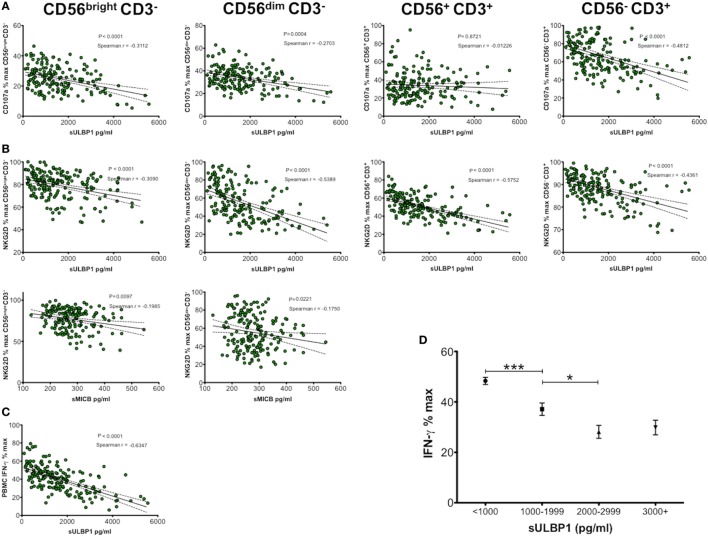
Figure 2.
Soluble NKG2D ligand (sNKG2DL) effect on NK group 2, member D (NKG2D) and CD107a expression by CD56bright CD3−, CD56dim CD3− natural killer (NK) cells, CD56+ CD3+ NKT cells, CD56− CD3+ T cells, and IFN-γ production by peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs). (A) Correlation and linear regression analysis of sULBP1 concentration effect on CD107a expression. (B) Correlation and linear regression analysis of sULBP1 and sMICB concentration on NKG2D expression. (C) Correlation and linear regression analysis of sULBP1 effect on production of IFN-γ by PBMCs. PBMCs were incubated with 50% cord blood plasma (CBP) (n = 181) or media only for 48 h and then stimulated with PMA and ionomycin. IFN-γ in culture supernatants and sNKG2DLs in CBP was measured by ELISA and expression of CD107a and NKG2D on the different cell types was measured by flow cytometry. P-values for Spearman r correlations are indicated. (D) Increasing concentration of soluble ULBP1 decreases potential IFN-γ production by NK cells in a dose-dependent manner (n = 181). Each experiment was repeated with four different PBMC donors and data points represent donor means. Statistical analysis (D) was performed using Mann–Whitney test ± SEM (*P ≤ 0.05 and ***P < 0.001).