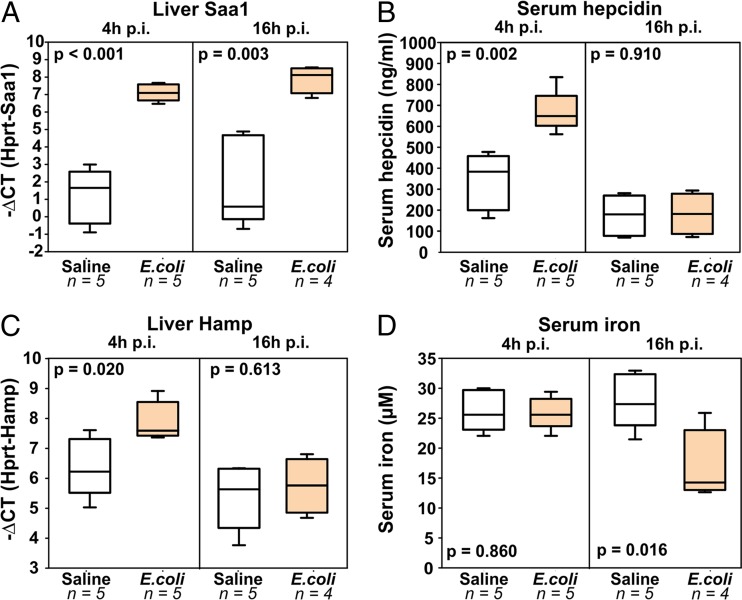
FIG 2.
E. coli infection rapidly induces systemic inflammation, increases hepcidin levels, and causes hypoferremia. WT mice were injected i.p. with either saline or 104 CFU of E. coli (isolate 1) per mouse. Tissues were collected at 4 and 16 h postinfection for analysis. We measured liver Saa1 levels as a marker of systemic inflammation (A), hepcidin protein (B), hepcidin mRNA (C), and the serum iron concentration (D). Inflammation induces the initial rise in serum hepcidin protein and mRNA levels, followed by hypoferremia and a reactive decrease in hepcidin protein and mRNA levels.