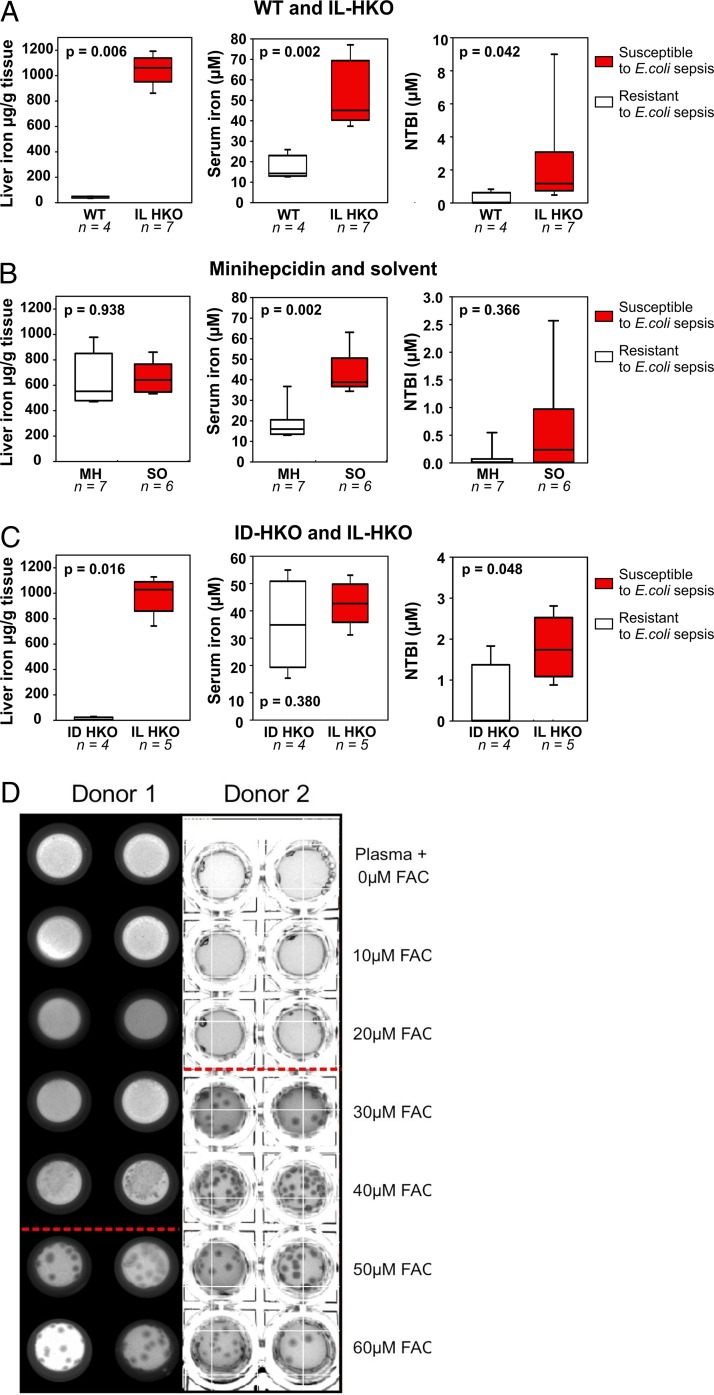
FIG 4.
Non-transferrin-bound iron (NTBI) rather than total iron promotes susceptibility to E. coli sepsis. (A to C) Liver iron, serum iron, and non-transferrin-bound iron measurements for WT (white boxes) and IL-HKO (red boxes) mice (A), IL-HKO mice treated i.p. either with a single dose of solvent (red boxes) or 100 nmol minihepcidin (white boxes) at 14 h prior to tissue collection (B), or IL-HKO (red boxes) and ID-HKO (white boxes) mice (C). All mice were infected i.p. with 104 CFU of E. coli (isolate 1) per mouse, and tissues were collected at 14 to 16 h postinfection (p.i.). IL, iron loaded; ID, iron depleted. (D) Human plasma was supplemented with 0 to 60 μM ferric ammonium citrate (FAC) and used to make agar plates. E. coli isolate 1 was plated and incubated for 38 to 41 h at 37°C, and the number of bacterial CFU was documented by photography. The results of two separate experiments using plasma from different donors are shown. Conditions below the red line had detectable NTBI.