Fig. 2.
Downregulation of genes involved in the host immune response is observed through transcriptomic analysis.
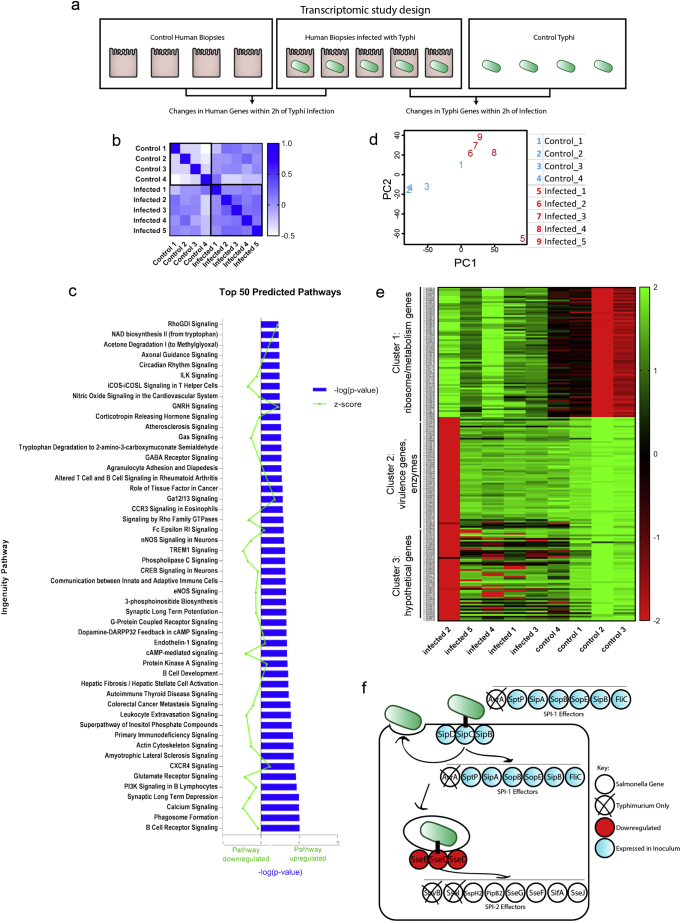
(A) A schematic overview of the transcriptomic study design using human biopsies.
(B) Similarity matrix compares gene expression between samples to show that control and infected biopsies behaved like other control or infected biopsies without extensive variation.
(C) Ingenuity Pathway analysis reveals clustering of genes in the top 50 predicted pathways; −log (p-value) is shown in blue; the z-score indicating pathway upregulation or downregulation is shown in green.
(D) Principle components analysis shows that bacterial gene expression changes cluster based on infecting group or control group (C).
(E) Bacterial genes clustered in three significant groups based on transcriptional changes. Cluster one encompasses genes required for gene expression; cluster two contains virulence genes, and cluster three contains a mix of hypothetical and virulence genes.
(F) Comparison of genes utilized during STM infection overlaid with the gene expression profile of STY bacteria during invasion; it is important to note that genes expressed in our inoculum were not differentially expressed at 2 h invasion. SPI-1 effectors are important for facilitating invasion and are expressed early on; SPI-2 effectors are expressed later in infection and are important for intracellular survival. The SPI-2 genes sseB, sseC, sseD are downregulated at 2 h invasion of intestinal biopsies.