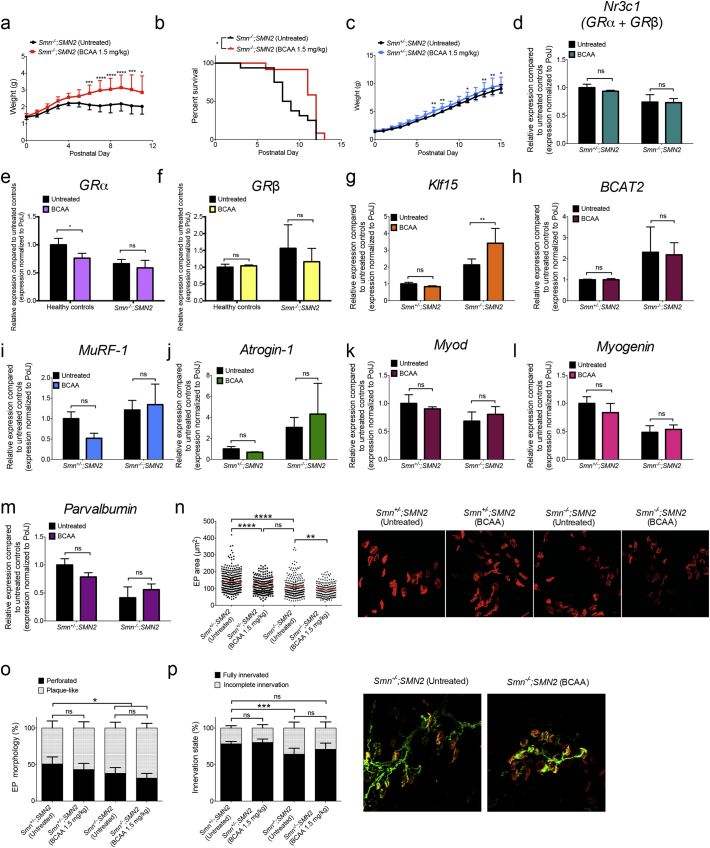
Fig. 8.
BCAA supplementation improves disease phenotypes of severe SMA mice. Smn−/−;SMN2 mice and healthy controls were treated with BCAAs (1.5 mg/kg) starting at P5. a. Weight curves of BCAA-treated Smn−/−;SMN2 mice vs. untreated animals. Data represent mean ± SD; n = 12–16 animals per group; two-way ANOVA; *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. b. Lifespan of BCAA-treated Smn−/−;SMN2 mice vs. untreated animals. Data represent Kaplan-Meier curves; n = 10–16 animals per group; Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test; p = 0.0159. c. Weight curves of BCAA-treated healthy controls vs. untreated animals. Data represent mean ± SD; n = 14–18 animals per group; two-way ANOVA; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. qPCR analysis of (d) Nr3c1, (e) GRα, (f) GRβ, (g) Klf15, (h) Bcat2, (i) MuRF-1, (j) atrogin-1, (k) MyoD, (l) myogenin and (m) parvalbumin mRNAs expression in triceps of BCAA-treated P7 Smn−/−;SMN2 mice and healthy controls compared to untreated animals. d-m: Data represent mean ± SD; n = 3–4 animals per group; two-way ANOVA; **p < 0.01; ns = not significant. n. Motor endplate area in TAs of BCAA-treated P7 Smn−/−;SMN2 mice and healthy littermates compared to untreated animals. Data represent scatter plot ± SD; n = 198–324 endplates from 4 animals per group; one-way ANOVA; **p < 0.01, ****p < 0.0001; ns = not significant. o. Motor endplate morphology (plaque-like or perforated) in TAs of BCAA-treated P7 Smn−/−;SMN2 mice and healthy controls compared to untreated animals. Representative images of endplates from untreated and BCAA-treated Smn−/−;SMN2 mice and healthy littermates. p. Innervation status of motor endplates in TAs of BCAA-treated P7 Smn−/−;SMN2 mice and healthy controls compared to untreated animals. Representative images of NMJs from untreated and BCAA-treated Smn−/−;SMN2 mice. o-p. Data represent mean ± SD; n = 4 animals per group; two-way ANOVA; *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001; ns = not significant.