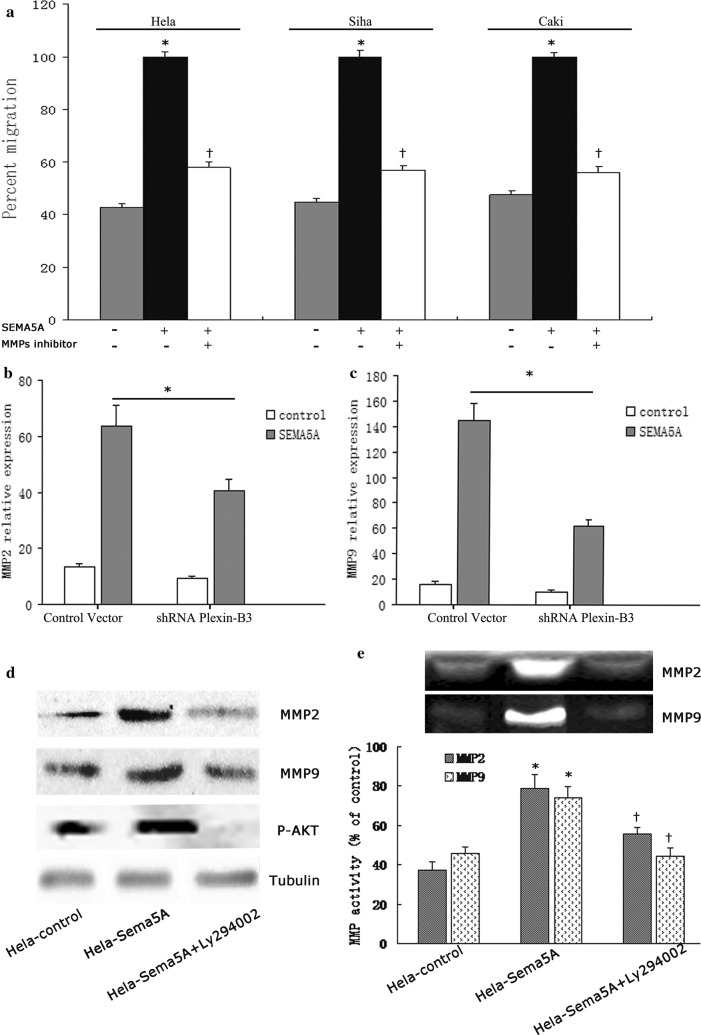
Fig. 7.
SEMA5A induces cervical cancer cell invasion by stimulating MMP activity via plexin-B3 and PI3K/AKT. a Matrigel invasion assays were performed on cervical carcinoma cell line Hela stimulated with or without SEMA5A (100 ng/mL) in the absence or presence of the MMP inhibitor GM6001 (1 μM). Data are shown as the percentage of invaded cells relative to the control. SEMA5A-induced invasion was dependent on MMP activity as evidenced by the decrease in SEMA5A-induced invasion with GM6001 treatment. *P < 0.05 vs. the respective controls. †P < 0.05 vs. the respective SEMA5A-treated cells. Plexin-B3 knockdown significantly decreased SEMA5A-induced (b) MMP-2 and (c) MMP-9 expression as assessed by real-time RT-PCR. d Western blot analysis showed a marked increase in the protein expression of MMP-2, MMP-9, and p-AKT in HeLa-Sema5A cells compared with HeLa-control cells. The PI3K inhibitor LY294002 reduced MMP-2, MMP-9, and p-AKT expression in HeLa-Sema5A cells. e Summary of MMP-2 and MMP-9 zymography data. Zymography data are representative of two independent experiments. The PI3K inhibitor LY294002 reversed the increase in MMP-2 and MMP-9 activities in HeLa-Sema5A cells. *P < 0.05 vs. the respective HeLa-control cells. †P < 0.05 vs. the respective HeLa-Sema5A cells. Columns represent the mean of two triplicate experiments; bars represent the standard error. MMP matrix metalloproteinase, p-AKT phosphorylated AKT, PI3K phosphoinositide 3-kinase, RT-PCR reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction, SEMA5A semaphorin 5A