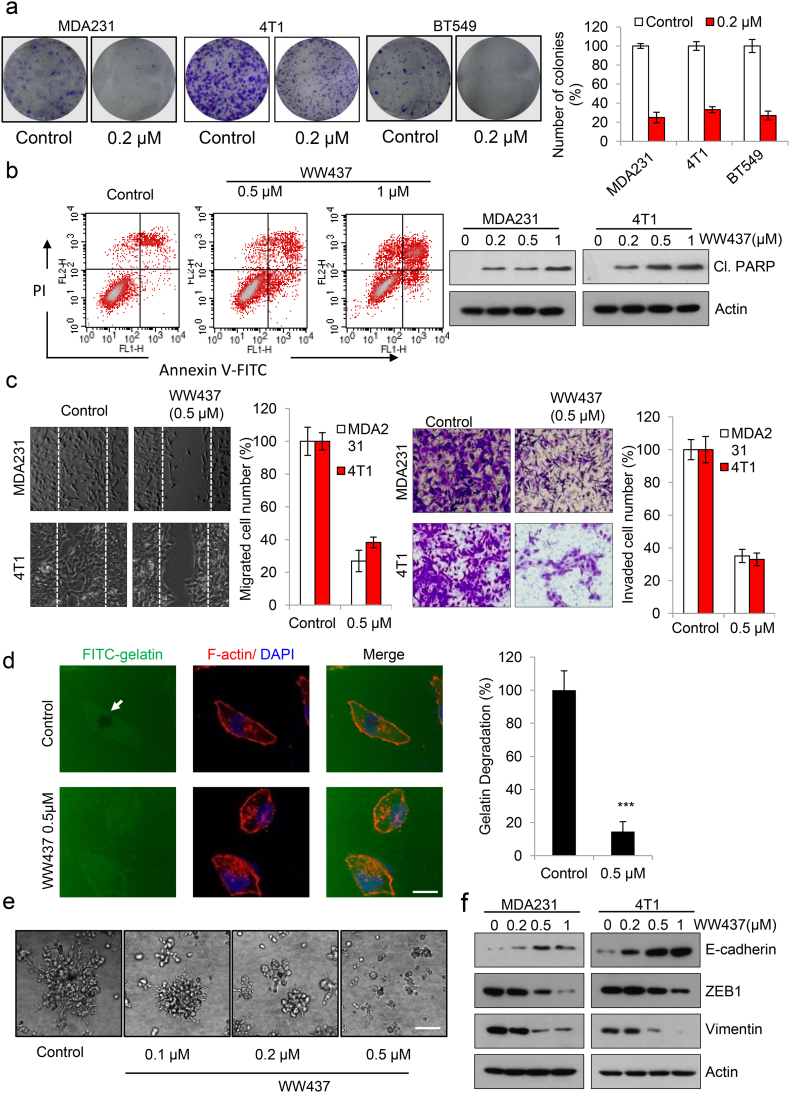
Fig. 2.
WW437 displays potent tumor growth and metastasis-inhibitory effects on breast cancer cells. (a) WW437 significantly inhibited breast cancer cell colony formation. Breast cancer cells were seeded on six-well plates. After 12 h, cells were treated with indicated concentrations of WW437. On day 10, the number of colonies were counted. Results represent the average of three replications. The bars indicate the mean ± SD. (b) Apoptosis was assessed by Annexin V/PI staining and flow cytometry (left panel). Cleaved PARP was evaluated by western blot (right panel). (c) WW437 (0.5 μM) inhibited cell migration and invasion in two highly malignant breast cancer cell lines MDA231 and 4 T1. Left, representative images and quantification of the migration assay; right, representative images and quantification of the invasion assay. The bars indicate the mean ± SD. (d) MDA231 cells were seeded on coverslips (procoated with FITC conjugated gelatin). After treated with WW437 for 12 h, F-actin was stained with phalloidin (red) and nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Areas of gelatin degradation were quantified using Image-Pro Plus 6.0 software. Scale bar, 10 μm. The bars indicate the mean ± SD. Statistically significant differences (Student's t-test), ***, P < 0.001. (e) 3D culture assay. MDA231 cells were seeded onto solidified Matrigel. After 30 min, medium containing 10% Matrigel and various concentrations of WW437 were added on top of the cells. The Matrigel-medium mixture was replaced every other day. Four days later, cells were photographed. Scale bar, 40 μm. (f) The effect of WW437 on EMT related protein. Western blot analysis was performed with indicated antibodies.