FIGURE 1.
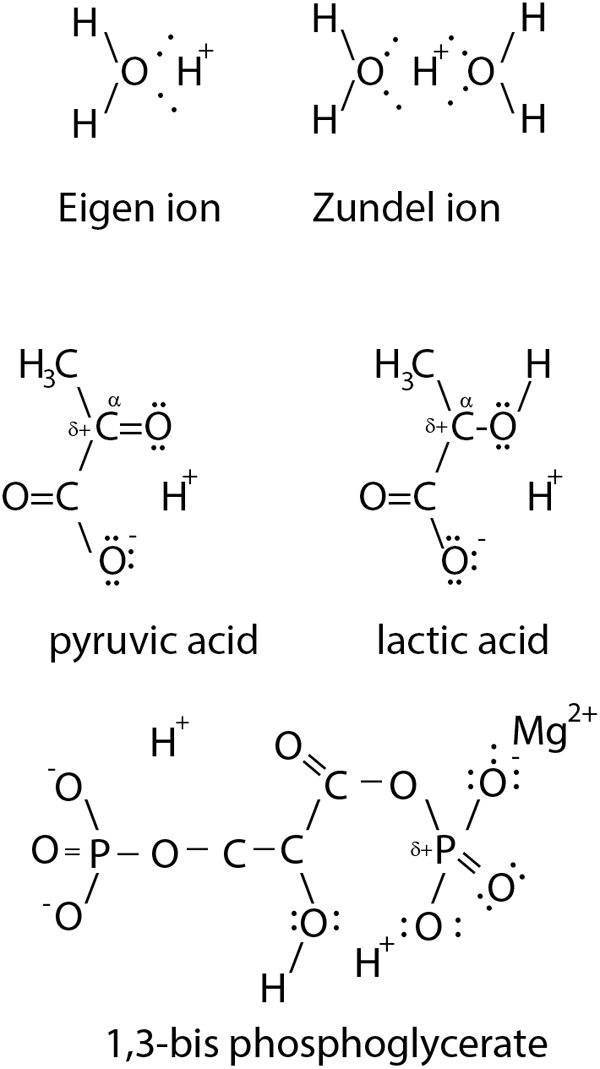
Illustration of a disolvated H+. In solution H+ is solvated (Eigen ion) usually disolvated by 2 H2O (Zundel ion). The α-C bound O-atom of monocarbonic acids, such as lactic acid and pyruvic acid, intra-molecularly disolvate the H+. The monocarbonic acids share the common characteristic of a partially positively charged (δ+) α-C atom to allow nucleophile substitution. Similarly, 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate uses O atoms to disolvate two protons.
