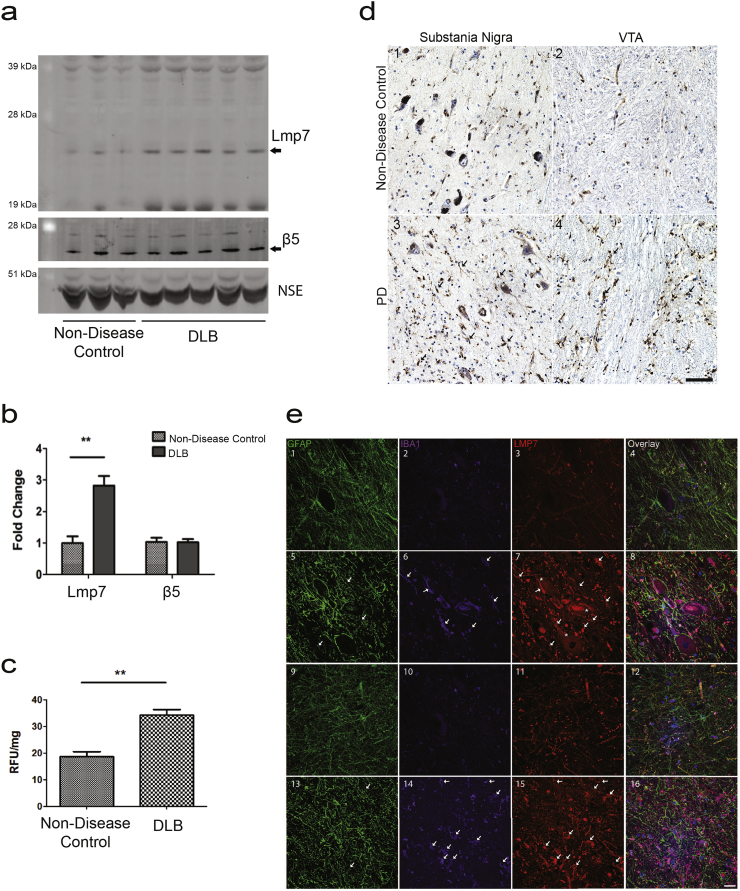
Fig. 4.
The Immunoproteasome in Human Disease Driven by α-Synuclein Aggregation. (a) Representative western blot analysis in human DLB and non-disease control brains for Lmp7 and the proteasome protein β5. (b) Densitometric analysis of western blots normalized to the levels of NSE protein indicate a significant increase (**p < 0.01, t-test) in Lmp7 levels in DLB brains (n = 5) compared with controls, (n = 3). (c) Concomitant with the increase in Lmp7 protein levels the chymotrypsin-like activity, a proxy for immunoproteasome activity, is increased by 189% in DLB brain compared with control brain (**p < 0.01, n = 3, t-test). (d) Immunohistochemical staining revealed increased immunoreactivity for Lmp7 in PD substantia nigra and VTA. (d1) Representative staining for Lmp7b in control substantia nigra and (d2) VTA. Increased Lmp7 staining in both neurons (asterisks) and glia (arrows) in PD substantia nigra (d3) and VTA (d4). Nuclei were counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Scale bar = 50 μm. (e) Co-localization of Lmp7 with glial markers. Representative fluorescent staining for the astrocyte marker, GFAP; microglial marker, IBA1; and Lmp7. Overlay of GFAP, IBA1, LMP7 and Hoechst nuclear stain is displayed in the right column. Staining in non-disease control substantia nigra (e1–4) and in VTA (e5–8). Increased staining for Lmp7 in the PD substantia nigra (e9–12) and in the VTA (e12–16). Lmp7 co-localized with both astrocytes and microglia. Staining increased in glial processes and soma (arrows) and neurons (asterisks) in PD substantia nigra relative to normal controls. Lmp7 staining increased in astrocytes and microglia (arrows) of PD VTA relative to non-disease controls. Scale bar = 20 μm.