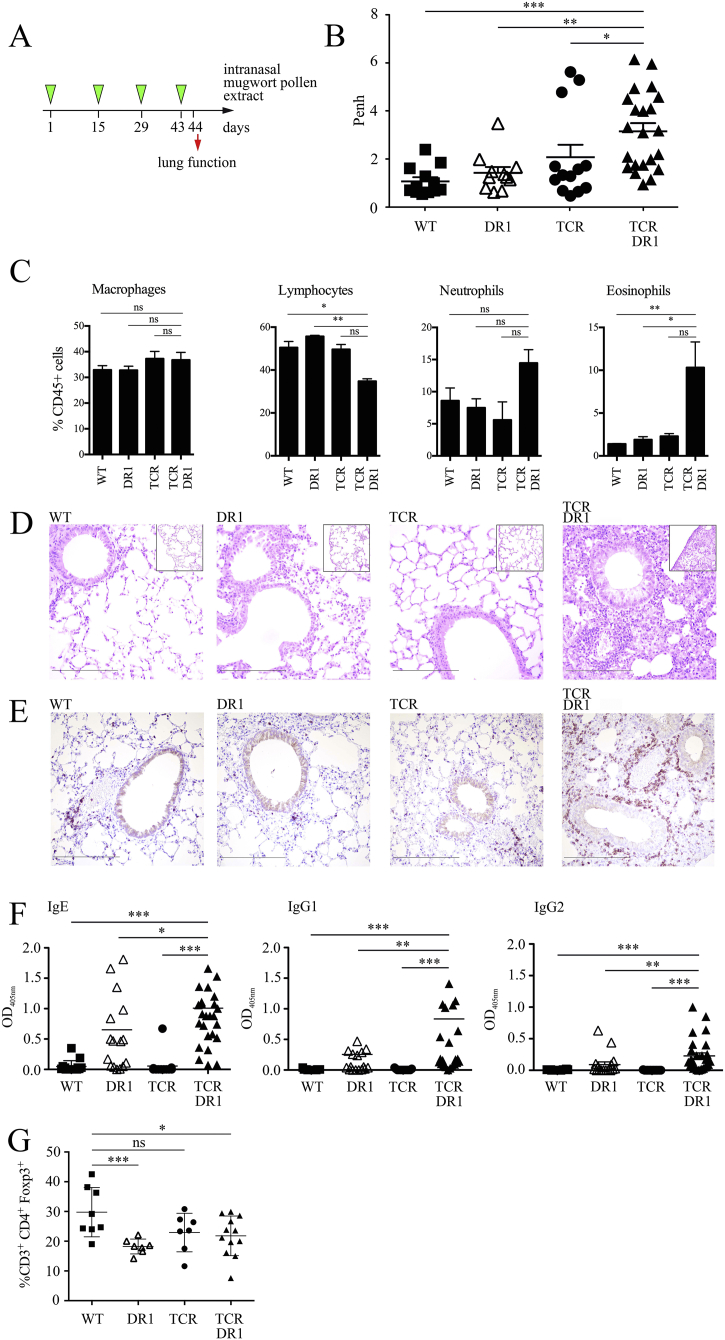
Fig. 3.
Severe lung pathology in TCR-DR1 mice upon intranasal exposure to aqueous mugwort pollen extract. A, Experimental design: Intranasal exposure of mice (WT, DR1, TCR, or TCR-DR1) to four doses of aqueous mugwort pollen extract (450 μg in 20 μl) at bi-weekly intervals. B, Allergen-specific airway hyperreactivity was measured 24 h after the last exposure by inhalation of 1% nebulized aqueous mugwort pollen extract aerosol and the mean enhanced pause (Penh) was determined by unrestricted whole body plethysmography (Buxco). Symbols represent individual mice. C, Shown are flow cytometric analyses of BALF cells gated on the indicated cell populations. D, H&E and E, immunohistochemical CD3 stainings of lung tissues analyzed by light microscopy, size bars 100 μm. F, Allergen-specific serum Ig levels (day 44). G, Percentages of CD3+CD4+Foxp3+ positive T cells after exposure. Data show the summary (B, F, G) or are representative (C, D, E) of 12 (for wild-type (WT), 11 for DR1, 13 for TCR and 22 for TCR-DR1) mice per group of three independent experiments (B–E) or 15 (for WT, 17 for DR1, 13 for TCR and 28 for TCR-DR1) mice per group of five independent experiments (F), or 12 for TCR-DR1 (except 8 for WT and 7 each for DR1 and TCR, respectively) mice of two independent experiments (G). *p < .05, **p < .01, ***, p < .001. ANOVA and Tukey's multiple comparison test.