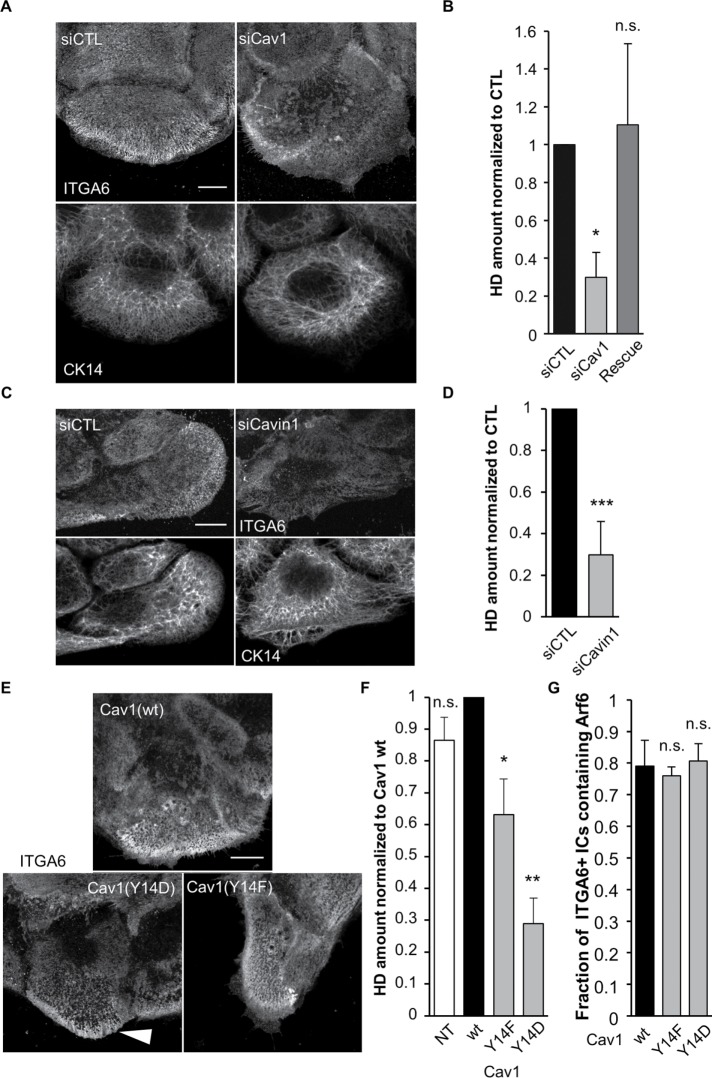
FIGURE 4:
Caveolae proteins are essential for proper HD organization. (A–D) Confocal images of the basal membrane and associated quantification of the amount of HDs (from ITGA6 staining) at the basal membrane of cells transfected with control (A, B) Cav1 siRNAs or (C, D) Cavin1 siRNAs then immunostained for ITGA6 and CK14 (A, C). The Rescue column (B) corresponds to cells transfected with Cav1 siRNAs plus a plasmid encoding wild-type RFP-Cav1 mutated to be Cav1 siRNA resistant. Scale bar = 10 µm. Data are from three independent experiments with (B) number of cells = 50, 65, and 46 and (D) N = 31 and 31. Student’s t tests: siCTL vs. (B) siCav1 or Rescue and (D) vs. siCavin1. (E) Confocal images of the basal membrane of cells expressing wt or mutant forms of RFP-Cav1 immunostained for ITGA6 and CK14. Scale bar = 10 µm. The white arrowhead highlights integrin accumulation at the edge of a Cav1(Y14D) expressing cell. (F) Quantification of the amount of HDs (from ITGA6 staining) at the basal membrane of cells expressing Cav1 mutant forms from three independent experiments; number of cells = 29, 59, 58, and 59. Student’s t tests: Cav1(wt) vs. NT, Cav1(Y14F), or Cav1(Y14D). (G) Quantification of the presence of Arf6 in ITGA6-enriched intracellular compartments in cells expressing mutant forms of Cav1 from three independent experiments; number of cells = 27, 38, 33. Student’s t tests: Cav1(wt) vs. Cav1(Y14F) or Cav1(Y14D).