Figure 2.
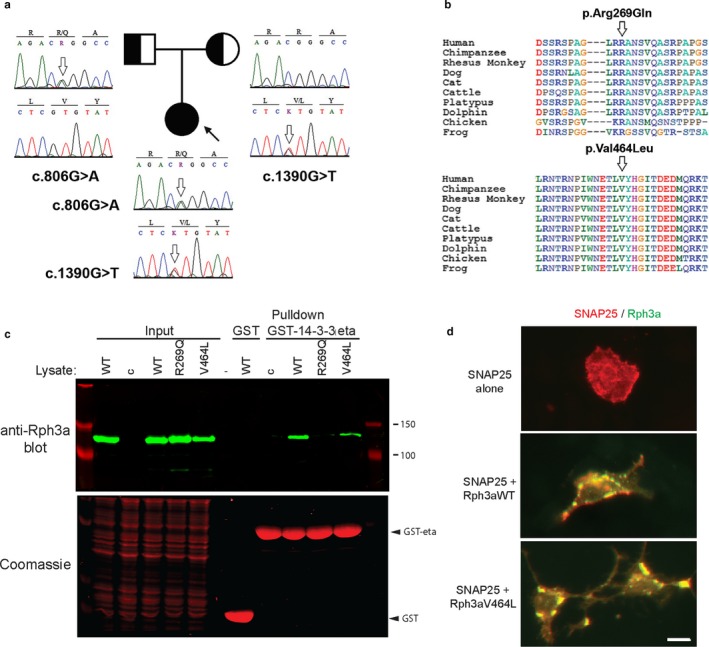
Pedigree, alignment of variants and expression studies. a. Family tree showing the segregation of RPH3A variants. b. Sequence alignments across species showing the location of the variants at conserved domains of the protein. c. Assay of rabphilin 3a–14‐3‐3 binding. Rabphilin 3a (Rph3a) variants were expressed in HEK cells and the cell lysates incubated with GST or GST‐14‐3‐3 eta beads. Rabphilin pulled down on the beads was detected by immunoblotting with anti‐rabphilin 3a antibody (upper panel) and GST‐fusion proteins were detected by Coomassie staining (lower panel). Control (c) is the cell lysates of sham‐transfected cells. Rabphilin 3a pulldown by GST‐14‐3‐3 eta was severely reduced by the Arg269Gln mutant, but only marginally by Val464Leu compared to rabphilin 3a WT. d. Rabphilin 3a colocalization with SNAP25. HEK cells transfected with rabphilin 3a‐YFP, Rab3a and/or SNAP25 were immunostained with SNAP25 antibodies. When expressed alone, SNAP25 was diffusely distributed, but when co‐expressed it partially colocalized with rabphilin in vesicular bodies (yellow puncta) near the cell membrane. Both rabphilin 3a WT and Val464Leu induced a similar redistribution of SNAP25. The calibration mark represents 10 µm
