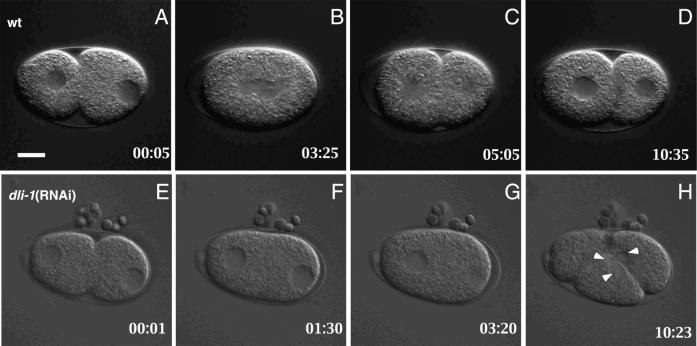
Figure 4.
Comparison of pronuclear migration in wild-type and dli-1(RNAi) embryos. All images are oriented with anterior to the left. (A–D) Wild-type embryo; female (anterior) and male (posterior) pronuclei begin migration before regression of the pseudocleavage furrow. The two pronuclei meet and fuse before nuclear envelope breakdown. (E–H) In the majority (16/19) of dli-1(RNAi) embryos harvested from injected wild-type mothers (shown) and 100% of embryos harvested from injected dli-1 heterozygous mothers (n = 19), pronuclear migration does not occur. (F) At the completion of pseudocleavage furrow regression, neither pronucleus has initiated migration. (G) At a time point equivalent to that in B in which the wild-type embryo is in metaphase, no pronuclear migration is apparent, and the male pronucleus has undergone NEB before female pronuclear NEB. (H) Multiple nuclei were formed in all dli-1(RNAi) embryos observed (arrowheads). Timestamps are relative to completion of anterior cytoplasmic contractions. In a wild-type embryo almost immediately after this, the female pronucleus initiates posteriorward migration. Bar, ∼10 μm.