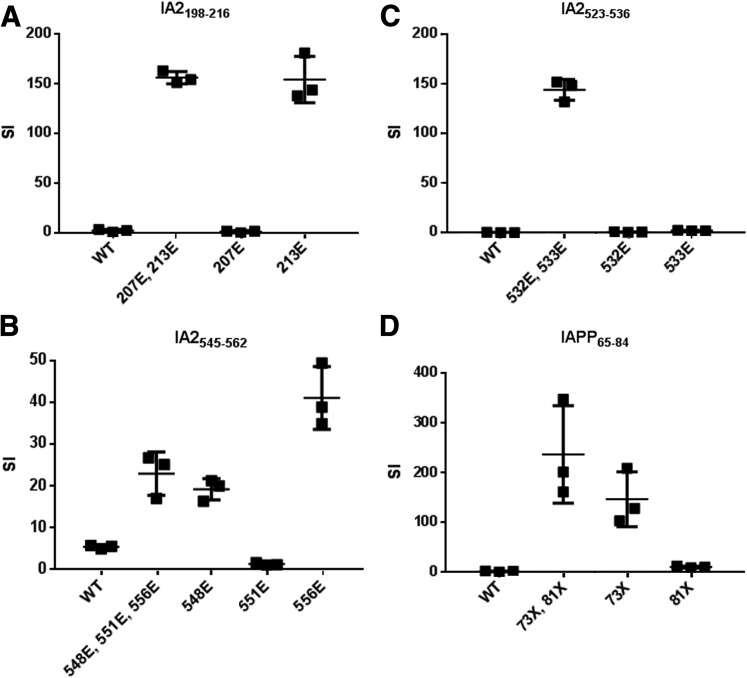
Figure 2.
Single residues modulate recognition of posttranslationally modified peptides by T cells. A: For IA-2198–216, peptides that lacked a glutamate at residue 213 (wild type [WT] and 207E) could not elicit proliferation of the T-cell clone, indicating that this modification is required for recognition. B: For IA-2545–562, a peptide with only a glutamate at residue 556 elicited optimal proliferation of the T-cell clone, indicating that modification of residues 548 and 551 are not required for recognition. C: For IA-2523–536, peptides that lacked a glutamate at either residue 532 or residue 533 (WT, 532E, and 533E) could not elicit proliferation of the T-cell clone, indicating that both modifications are required for T-cell recognition. D: For IAPP65–84, peptides that lacked a citrulline at residue 73 (WT and 81X) could not elicit proliferation of the T-cell clone, indicating that this modification is required for recognition. The results shown are stimulation index (SI) values, calculated in triplicate by normalizing the proliferation of each representative clone based on [3H] thymidine incorporation in unstimulated wells. Horizontal lines show means and error bars indicate SDs. Results are representative of T-cell clones isolated from multiple subjects with type 1 diabetes (n ≥ 3). In panels A–C, each “E” indicates a glutamic acid modification at the indicated amino acid position. In panel D, each “X” indicates a citrulline modification at the indicated amino acid position.