Figure 3. Key Figure.
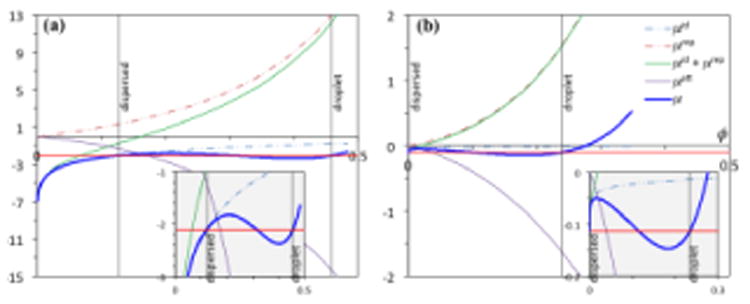
Decomposition of the chemical potentials of colloid and polymer models. (a) The chemical potential (μ) of a colloid suspension is given by Box 3 Equation [VI], with the ideal (μid; assuming νQ = νp), repulsive (μrep), and attractive (μrep) components, respectively, represented by the three terms on the right-hand side. Results for δ/σ = 0.15 and kBT/ε = 0.6 are shown. (b) The chemical potential of a polymer solution is shown on a per monomer basis (L = 100). μid/L = (1/L) ln ϕ; μrep/L is given by Box 4 Equation [V]; and μatt/L is given by Box 4 Equations [VI] – [VIII] (for δ/d = 0.5 and kBT/ε = 2.4). Abscissa: volume fraction ϕ; ordinate: chemical potentials and their components in units of kBT. Horizontal red lines dissect the μ versus ϕ curves (blue) with equal areas; ϕ values for the dispersed and droplet phases are indicated by vertical black lines; the ϕ value for the dispersed phase of the polymer solution is so small that a vertical line cannot be distinguished from the ordinate axis. A view of the dissection, enlarged in the vertical direction, is shown as insets (gray shading).
