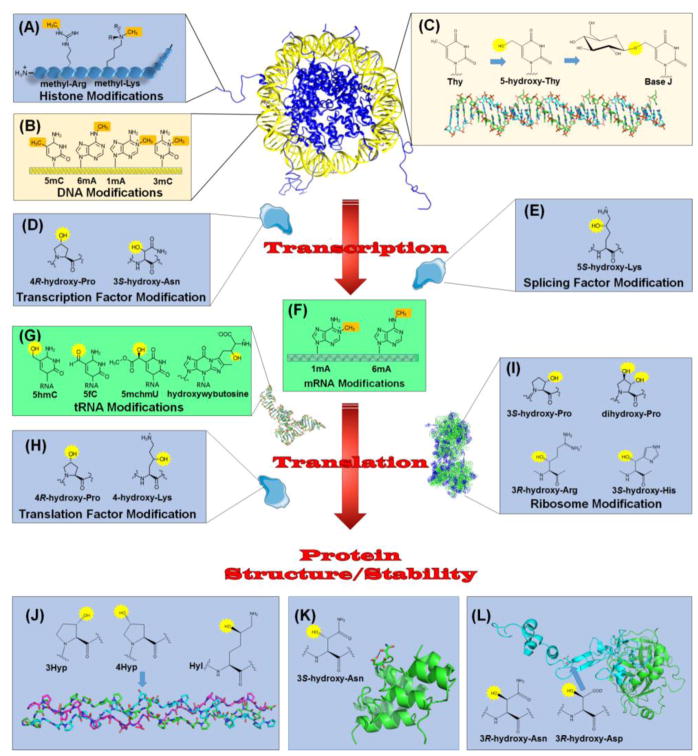
Figure 2.
Relationship of 2OG-Dependent Oxygenases to the Central Dogma. Chromatin regulation involves methylation of (A) specific Lys and Arg residues in the N-terminal tails of histones and (B) several types of bases in DNA. Demethylases and other 2OG-dependent oxygenases function to reverse these modifications. (C) Base J is a DNA modification found in certain kinetoplasts. Selected thymidine bases (Thy) are modified by a 2OG-dependent hydroxylase to form 5-hydroxy-Thy, then glycosylated by a separate enzyme. (D) Regulated RNA synthesis involves transcription factors, such as HIF, modified by 2OG-dependent hydroxylases. (E) An oxygenase also modifies a splicing factor as part of the maturation of precursor RNA. (F) 2OG-dependent enzymes remove methylation marks in mRNA. (G) Representatives of these enzymes demethylate, hydroxylate, and hypermodify bases in tRNA. (H) Translation factors undergo hydroxylations catalyzed by 2OG-dependent oxygenase. (I) Several hydroxylations are introduced into ribosomal proteins by these enzymes. In addition, other proteins are hydroxylated related to structure/stability. (J) Collagen contains 4R-hydroxy-Pro (4Hyp), 3S-hydroxy-Pro (3Hyp), and 5R-hydroxy-Lys (Hyl) residues synthesized by 2OG-dependent hydroxylases. The structure is shown for a collagen model peptide (PDB access code 3ABN) that is rich in Pro and Gly residues and contains 4Hyp (arrow); three peptides (depicted in green, cyan, and magenta) form a triple-helical structure. (K) Some ankyrin repeat domain (ARD) proteins undergo hydroxylation at the 3S position of Asn residues, leading to protein stabilization. The structure shown (PDB access code 2ZGD) is from a synthetic consensus sequence hydroxylated by FIH. (L) Activated factor IX (PDB access code 1PFX) has a large catalytic chain (green) and a small chain (cyan) containing an EGF domain with a 3R-hydroxy-Asp residue (arrow). Also shown is the structure of 3R-hydroxy-Asn. DNA bases are shown in yellow, RNA components are in green, and protein sidechains are in blue. The methylation sites targeted for hydroxylation (A, B, and F) and the introduced hydroxylations (C, D, E, G, H, I, J, K, and L) are highlighted in brown and yellow, respectively.