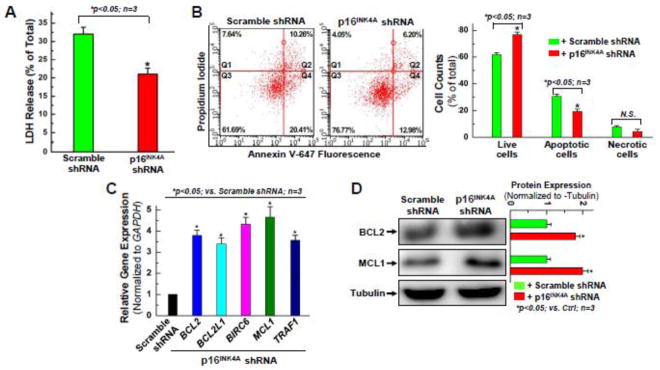
Figure 3. Knocking down the expression of p16INK4A exhibits an anti-apoptotic effect in aging hCPCs.
A. Aging hCPCs (AMC20) were infected with lentivirus expressing shRNA against p16INK4A, or scramble shRNA for 48 hours, challenged with 2 mM H2O2 for 3 hours, then evaluated by LDH assay. Data presented in this figure were mean values on a ratio of H2O2-induced LDH release to total LDH in cells with standard deviation (means ± SD). B. Human CPCs were infected with p16INK4A, or scramble shRNA for 48 hours, and challenged with 1 mM H2O2 for 1.5 hours, then evaluated by Annexin/PI FACS assay with quantitative analysis. C. Real time qPCR was performed to examine the expression of anti-apoptotic genes at the mRNA level after p16INK4A was knocked down in hCPCs. D. Representative images and quantitative data of Western blot showing the expression level of anti-apoptotic proteins, including BCL2 and MCL1 after p16INK4A knockdown in hCPCs. Data were presented as means ± SD from 3 independent experiments (n=3); * indicates p<0.05 vs. scramble shRNA.