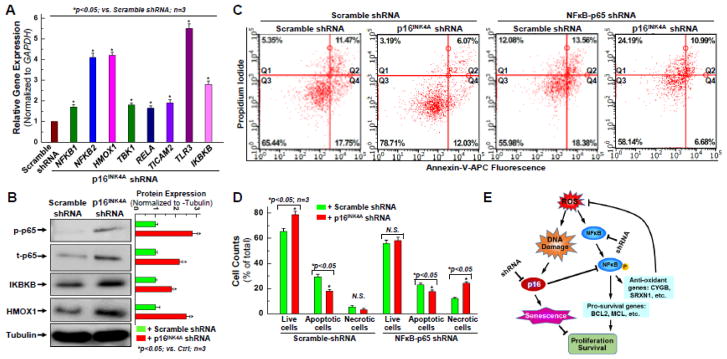
Figure 5. Up-regulation of NFκB signal pathway is associated with the rejuvenating effect of knocking down p16INK4A in aging hCPCs.
A. Real time qPCR was performed to examine the expression of NFκB signal pathway associated genes at the mRNA level after p16INK4A was knocked down in aging hCPCs. B. Representative images and quantitative data of Western blot showing the expression level of NFκB-associated proteins, including total and phosphorylated p65, IKBKB, and HMOX1 after p16INK4A was knocked down in aging hCPCs. C. Representative FACS analysis with annexin-V/PI staining showing H2O2-induced apoptosis in hCPCs stably expressing scrambled or NFκB-p65 shRNA following with or without knocking down p16INK4A. D. Quantitative data analysis for panel C. E. Descriptive diagram of proposed molecular mechanism underlying the rejuvenating effect of knocking down p16INK4A in aging hCPCs. Data were presented as means ± SD from 3 independent experiments (n=3); * indicates p<0.05 vs. scramble shRNA.