Figure 2. The radiolabeled signal in the cytosol is due to thiolation of tRNAs.
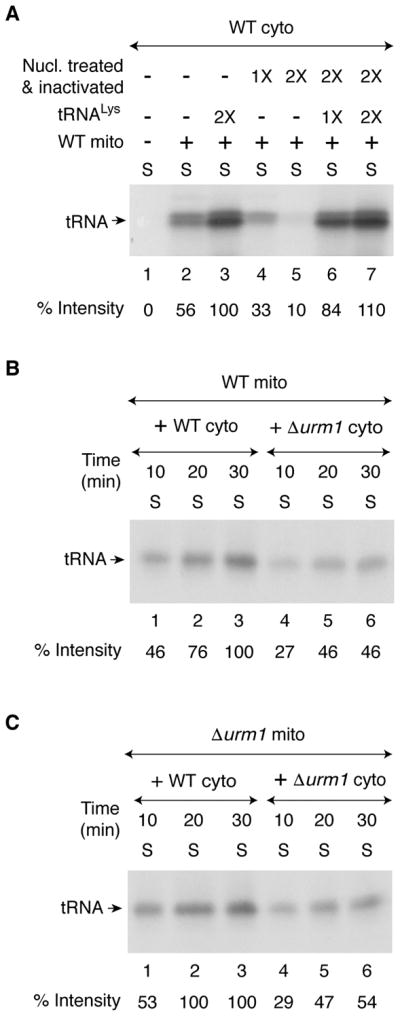
(A) As indicated, WT cytosol (200 μg) was treated with S7 micrococcal nuclease (1X = 450 units/ml) in the presence of 0.5 mM CaCl2 for 10 min at 30°C, and the nuclease was inactivated by the addition of EGTA (2 mM). Nuclease-untreated (lanes 1–3), or nuclease-treated and subsequently inactivated (lanes 4–7) cytosolic samples were supplemented with [35S]cysteine, nucleotides and iron as in Figure 1A legend. Reaction mixtures were incubated at 30°C for 30 min, with or without added mitochondria (200 μg) and purified yeast tRNALys (1X = 0.25 A260 unit). After centrifugation, the supernatant/cytosol fractions were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and autoradiography.
(B) WT mitochondria (200 μg) were added to WT or Δurm1 cytosol (200 μg), and reaction mixtures were incubated with [35S]cysteine, nucleotides and iron at 30°C for different time periods as indicated. After centrifugation, the resulting supernatant (cytosol) fractions were analyzed as in Figure 1A legend.
(C) Δurm1 mitochondria (200 μg) were added to WT or Δurm1 cytosol (200 μg) and reactions were carried out as in (B) above.
