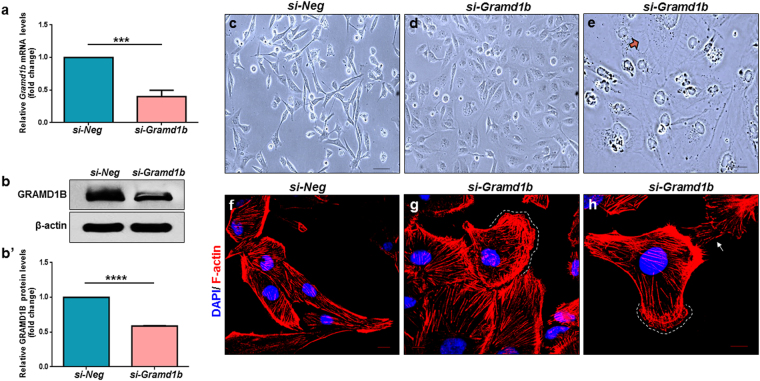
Figure 2.
GRAMD1B inhibition causes morphological changes of breast cancer cells. (a) si-Gramd1b knockdown decreases Gramd1b mRNA levels. Data is represented as mean ± SEM of n = 4. (b-b’) A decrease in GRAMD1B protein levels is also observed in Gramd1b knockdown cells. Data is represented as mean ± SEM of n = 3. (c,d) Gramd1b knockdown transforms the parental spindle-shaped MDA-MB-231 cells into rounded and flattened cells. (Scale bar = 100 μm). (e) Note the presence of cell membrane protrusions on loss of GRAMD1B activity (arrow). (Scale bar = 50 μm). (f–h) Phalloidin staining of si-Gramd1b transfected cells reveals the presence of F-actin-rich membrane protrusions (arrow), accompanied by membrane ruffle formation (white dashed lines). (Scale bar = 10 μm). ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001.