Fig. 1.
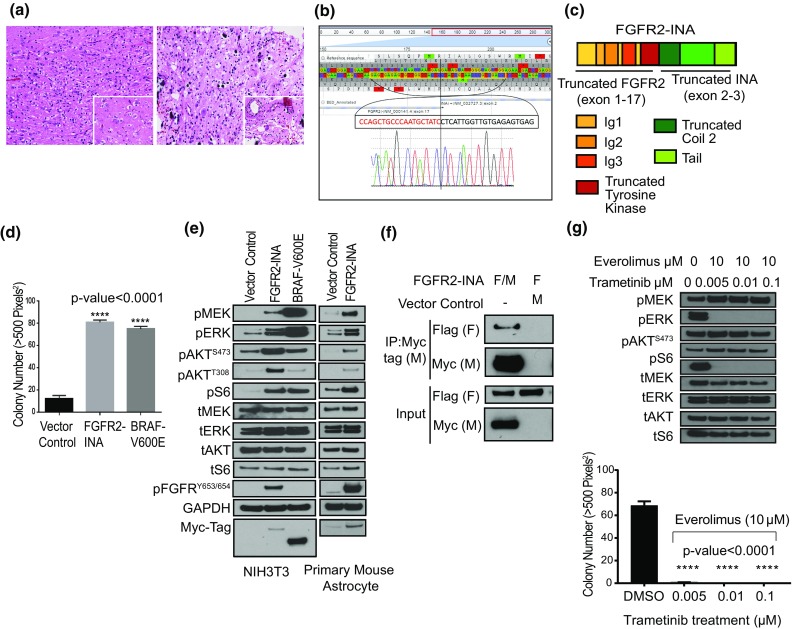
Histologic and sequencing characteristics of two MNGT harboring an FGFR2-INA fusion that activates the MAPK and PI3 K/mTOR pathways. a MNGT-1 (left) and MNGT-2 (right) contained small oligodendrocyte-like cells admixed with neurons surrounded by clear microcystic spaces (insets, 400X H&E), 200X H&E. b RNA-seq reads and confirmatory reverse complement Sanger sequencing of FGFR2-INA. c Structure of FGFR2-INA: FGFR2 exons 2–3 encode Ig-1, exons 4–5 encode Ig-2, exons 6–7 encode Ig-3 domains, and exons 9–17 encode a truncated tyrosine kinase domain (lacking three amino acids from FGFR2 exon-18). d Soft agar assay using NIH3T3 stably expressing FGFR2-INA, n = 10. Error bars represent SEM. e Western blot analysis of MAPK and PI3 K/mTOR pathway proteins in NIH3T3 and PMAs. ‘p’—phosphorylated; ‘t’—total protein. f Co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) assay with anti-Myc tag beads and co-transfecting HEK293 cells with Flag (F)- and Myc (M)-tagged FGFR2-INA, and F-FGFR2-INA with M- vector control. g Effect of combinatorial trametinib and everolimus treatment on FGFR2-INA-driven oncogenic signaling and growth in NIH3T3 cells
