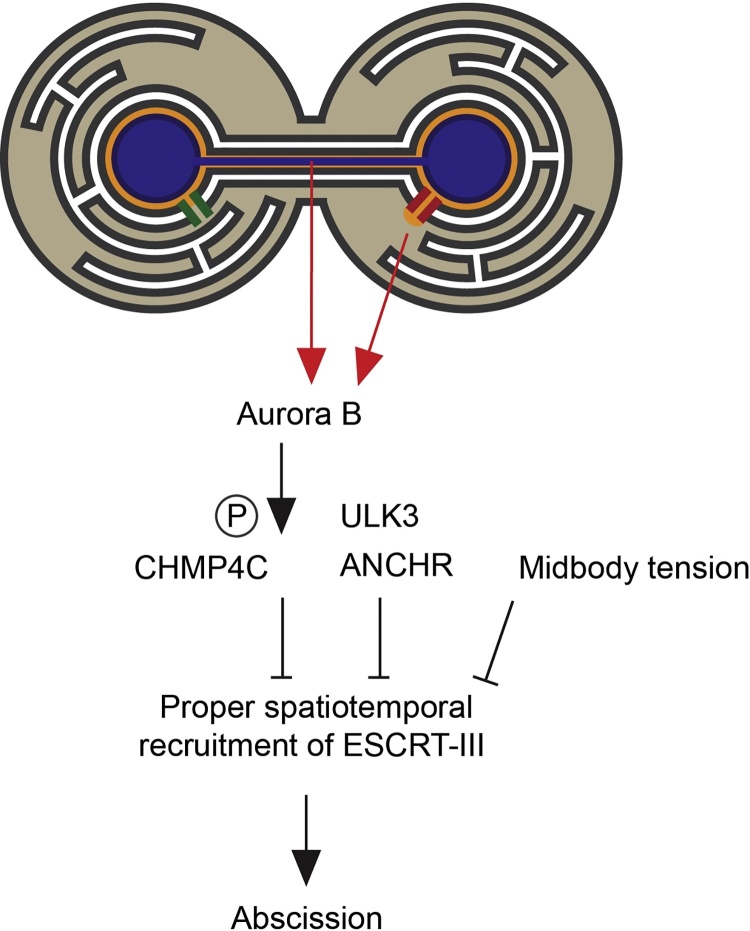
Fig. 4.
Role of ESCRT-III in the Aurora B mediated abscission checkpoint. Cartoon depicting triggers that initiate Aurora B-dependent abscission arrest. Elevated Aurora B downstream of chromosome segregation errors or NPC assembly defects (NPC in red, with indicated compartmentalisation breakdown, as per [179]) act to retard ESCRT-III-dependent abscission. Whilst a direct target of Aurora B is CHMP4C, ANCHR and ULK3 contribute to maintenance of this checkpoint. This checkpoint appears effected by spatiotemporal control over ESCRT-III assembly within the midbody; Aurora B phosphorylation directs CHMP4C to the Flemming body and ULK3 also drives ESCRT-III components onto the Flemming body. ANCHR acts to restrict VPS4 to the Flemming body and prevents it relocalising to the secondary ingression. Tension in the midbody can act to suppress ESCRT-III-assembly at the midbody and ESCRT-III-dependent abscission and this signalling acts though ULK3.