Figure 1.
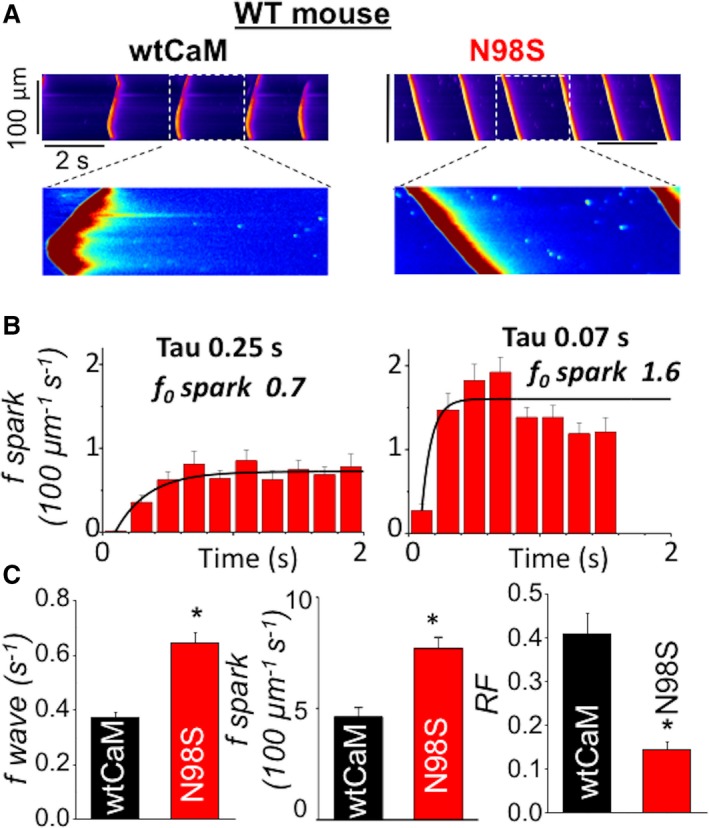
CPVT CaM N98S increased Ca wave frequency and shortened RyR2 refractoriness. A, representative line‐scan images of spontaneous Ca waves (SCWs) in permeabilized WT myocytes exposed to 100 nmol/L wtCaM or 100 nmol/L CPVT CaM N98S. Cytosolic Ca was clamped at ≈120 nmol/L with the slow Ca buffer EGTA. B, time‐dependent recovery of Ca sparks after occurrence of SCWs. Frequency of Ca sparks (f sparks) was calculated at 200 ms intervals. Recovery of Ca sparks was fitted with mono‐exponential curve with tau of 0.25 seconds for wtCaM and 0.07 seconds for N98S CaM, respectively. Ca sparks steady state levels (f0) were 0.7 (per 100 μm per second) for wtCaM and 1.6 (per 100 μm per second) for N98S CaM, respectively. C, Average data for SCW frequency, Ca spark frequency and refractoriness factor (RF) obtained from WT mouse ventricular myocytes permeabilized with wild‐type (wt) and CPVT (N98S) CaMs, respectively, n=38 to 58 cells, *P<0.05 vs wtCaM. Ca indicates calcium; CaM, calmodulin; CPVT, catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia; EGTA, ethylene glycol‐bis(β‐aminoethyl ether)‐N,N,N′,N′‐tetraacetic acid; RF, refractoriness factor; RyR2, ryanodine receptor 2; SCW, spontaneous Ca waves; WT, wild type.
