Fig. 2.
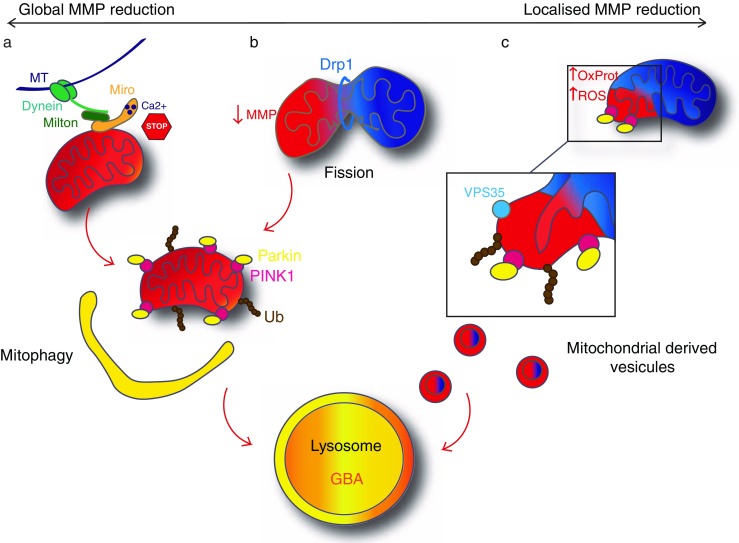
Organellar quality control. (a) Major mitochondrial dysfunction leads to a global MMP reduction (red). Miro1 ensures the arrest of mitochondrial transport along the microtubules (MT) by sensing the calcium concentration. PINK1 accumulates on the mitochondria and recruits Parkin. Parkin ubiquitinates various mitochondrial proteins that leads to the engulfment of mitochondria by the autophagosome. The autophagosome fuse with the lysosome and mitochondrial proteins become degraded by lysosomal enzymes. This process is called mitophagy. b Global mitochondrial dysfunction can be avoided by fission, induced by Drp1. The impaired daughter mitochondria (red) will then undergo mitophagy as well. c Mitochondria can also have a localised MMP reduction due to local increase of oxidised proteins (OxProt) or ROS. This leads to a budding of mitochondria-derived vesicles (MDVs) implicating a local activation of PINK1/Parkin pathway and recruitment of VPS35. MDVs then fuse with the lysosome. Healthy mitochondria (physiological MMP) are represented in blue, dysfunctional mitochondria (decreased MMP) are represented in red. Proteins in bold are linked to PD
