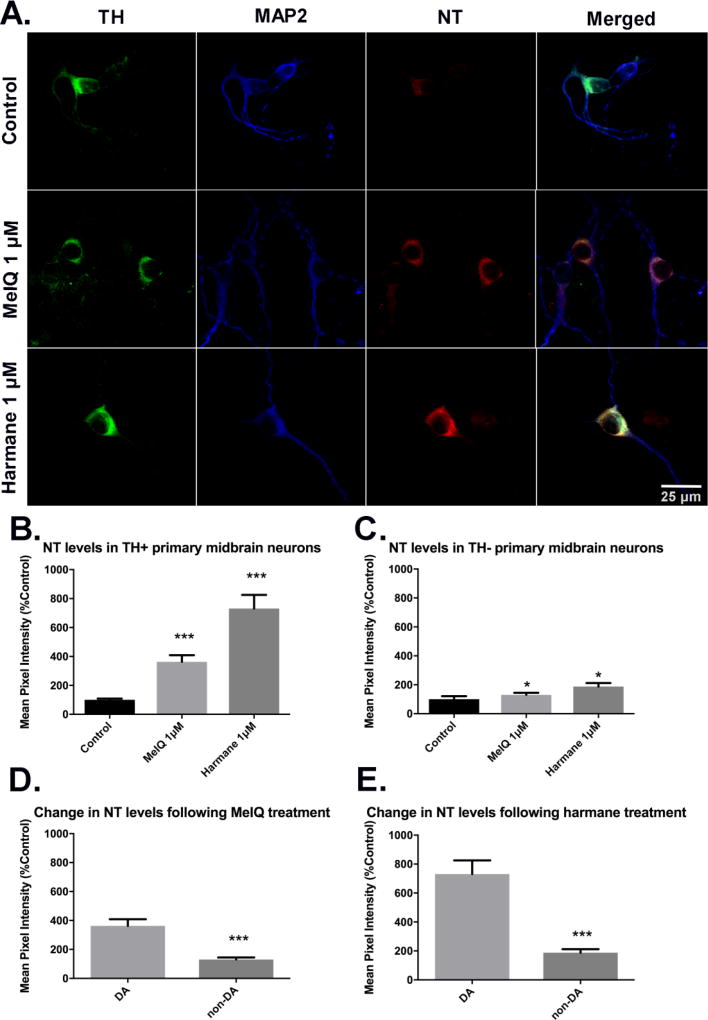
Figure 10. Harmane and MeIQ produce oxidative damage in DA neurons expressed through nitrotyrosine (NT) intensity.
A representative compound from the aminoimidazoaazarene subclass (MeIQ) and the α/β-carboline subclass (harmane) was chosen to test for the production of oxidative damage in dopaminergic neurons as evidenced by nitrotyrosine staining intensity. Representative images of untreated cultures or cultures treated with harmane (1 µM) or MeIQ (1 38 µM). Images captured via confocal microscopy after immunostaining using antibodies specific to TH (green), NT (red) and MAP2 (blue). Scale bars represent 25 µm (A). For quantification, NT fluorescence intensities in ROIs surrounding DA neuron cell bodies were quantified, then normalized to the mean value of the untreated culture. DA (B) and non-DA (C) neurons treated with harmane or MeIQ exhibited significantly increased NT levels. Data presented as the mean ± SEM; Kruskal-Wallis ANOVA with Dunn’s post-hoc test, *p<0.05, ***p<0.001 compared to control. Direct comparison between DA and non-DA neurons for each HCA shows (D, E) that DA neurons exhibited significantly increased oxidative damage vs. non-DA neurons after treatment. Data presented as the mean ± SEM; Mann-Whitney U-test, ***p<0.001 compared to DA. n = 71 – 141 ROIs analyzed/group over 3 biological repeats.