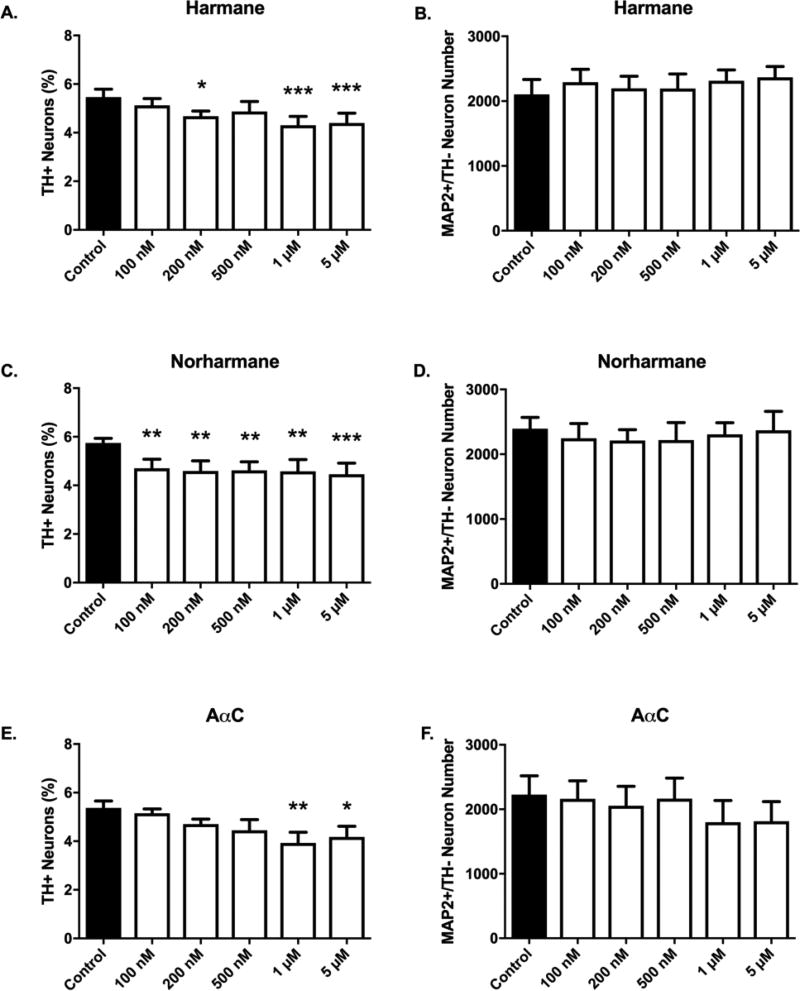
Figure 6. α/β-carboline treatment produces selective dopaminergic neurotoxicity.
Selective DA neuronal loss was detected for all tested aminoimidazoaazarene β-carboline (harmane or norharmane) and α-carboline (AαC) HCAs. The threshold dose required to elicit selective dopamine neuron toxicity is compound-dependent (A,C,E). Nondopaminergic neurons are not affected at tested doses (B,D,F) as evidenced by undetectable changes in MAP2+/TH− cell counts. Cells were stained for tyrosine hydroxylase, TH (green) to identify dopamine neurons and microtubule-associated protein 2 MAP2 (red) to identify all neurons. The percentage of TH+ neurons to MAP2+ neurons (TH+ Neurons %) was calculated to determine DA neuronal loss. Data presented as the mean ± SEM; one way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post-hoc test, *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p< 0.001 compared to control. n = 6/group.