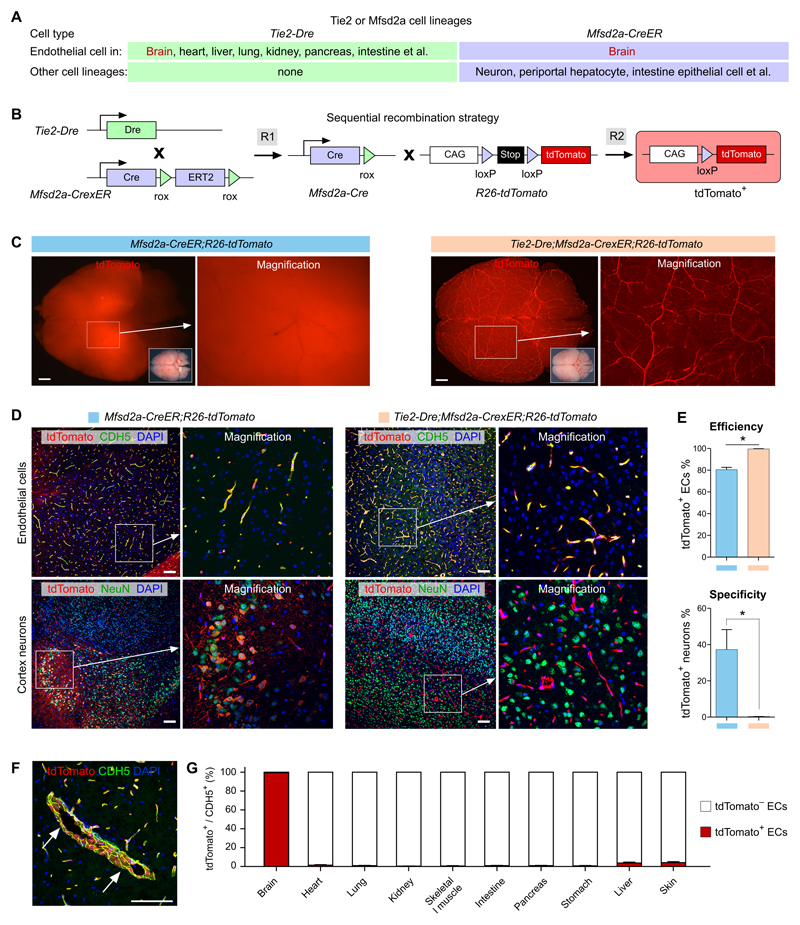
Figure 4. Specific and efficient brain endothelial cell targeting.
A, Cell lineages targeted by Tie2-Dre and Mfsd2a-CreER. B, Schematic showing the working principle for sequential Dre and Cre recombinations. The final readout is Cre-loxP recombination. C, Whole-mount fluorescence view of brains from adult Mfsd2a-CreER;R26-tdTomato or Tie2-Dre;Mfsd2a-CrexER;R26-tdTomato mice. For Mfsd2a-CreER, Tamoxifen was induced at 6 weeks and samples were collected 2 days later. Inserts are bright-field images of brains. D, Immunostaining for tdTomato and CDH5 or NeuN on brain sections of Mfsd2a-CreER;R26-tdTomato or Tie2-Dre;Mfsd2a-CrexER;R26-tdTomato mice. E, Quantification of the percentage of tdTomato+ endothelial cells (ECs) or tdTomato+ neurons. Data are mean ± SEM.; *P < 0.05; n = 5. F, Immunostaining for tdTomato and CDH5 shows large brain vessels (arrow) are also tdTomato+. G, Quantification of the percentage of tdTomato+ vascular endothelial cells in different organs, collected from adult Tie2-Dre;Mfsd2a-CrexER;R26-tdTomato mice. Scale bars, 1 mm in C; 100 µm in D,F.