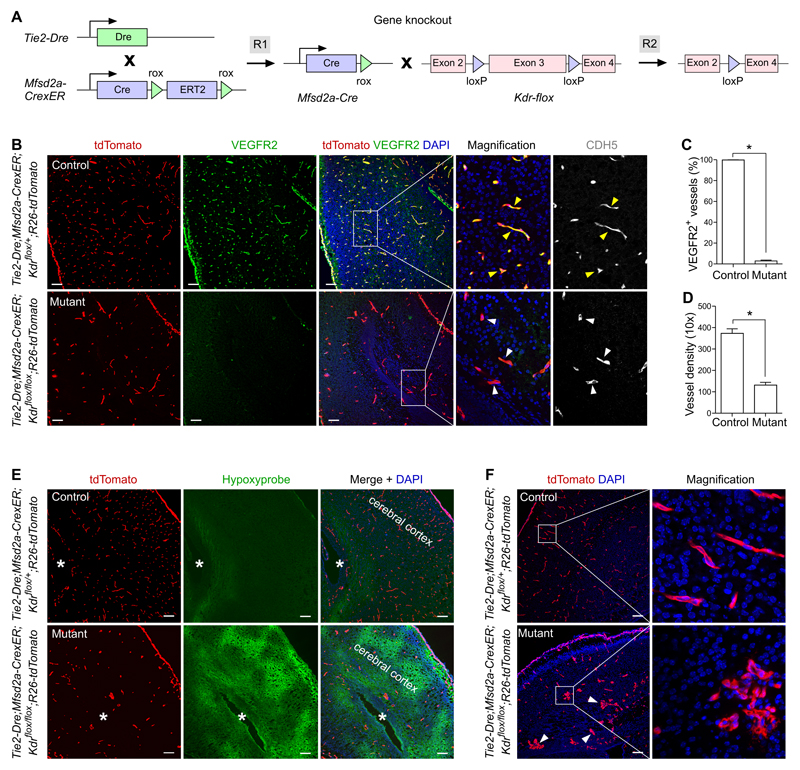
Figure 5. Specific knockout of VEGFR2 in brain endothelial cells.
A, Schematic figure showing the working principle for sequential Dre and Cre recombinations that ultimately delete the flox flanked Kdr gene in brain endothelial cells. B, Immunostaining for tdTomato, VEGFR2 and CDH5 on P0 brain sections of Tie2-Dre;Mfsd2a-CrexER;Kdrflox/+;R26-tdTomato (control) or Tie2-Dre;Mfsd2a-CrexER;Kdrflox/flox;R26-tdTomato (mutant) mice. Yellow arrowheads indicate VEGFR2+CDH5+ endothelial cells in the control brain; white arrowheads indicate VEGFR2–CDH5+ endothelial cells in the mutant brain. C, Quantification of VEGFR2+ endothelial cells in the control and mutant groups. Data are mean ± SEM.; *P < 0.05; n =5. D, Quantification of the vessel density in a 10x field. Data are mean ± SEM.; *P < 0.05; n = 5. E, Immunostaining for tdTomato and Hypoxyprobe on the control and mutant tissue sections. Asterisks indicate lateral ventricle in cerebral cortex. F, Immunostaining for tdTomato on brain sections shows abnormal vessels (arrowheads) in mutant compared with control. Scale bars, 100 µm. Each figure is representative of 5 individual samples.