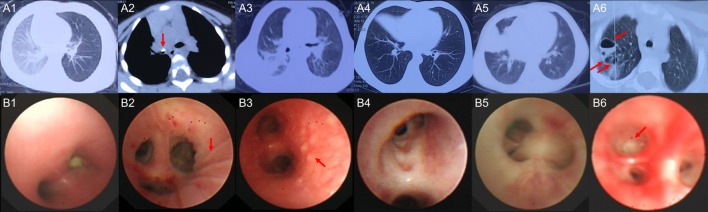
Figure 1.
The radiological images and bronchoscopic images of the subjects enrolled in sequencing. (A1) shows radiological image of control1, emphysema (air trapping) in the left lung was observed; (A2) shows radiological image of control 3, foreign body (red arrow) blocked the right main bronchus; (A3) shows radiological image of Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia (MPP) 1, patchy density shadows in the right lung were observed; (A4) shows radiological image of MPP3, atelectasis of the right middle lobe was found; (A5) shows radiological image of MPP4, which revealed large density shadows (consolidation) in the right middle lobe; (A6) shows radiological image of MPP6, multiple necrotizing sacs (red arrows) were observed in the right lung. The wall of the sacs was very thin, which was different from the lung abscess; (B1) is the bronchoscopic image of control 2, a peanut was observed in the right main bronchus, which blocked the airway; (B2) is the bronchoscopic image of MPP2, lines on mucosa (red arrow) were observed in the right upper lobe; (B3) is the bronchoscopic image of MPP5, which shows diffused mucosal nodules (red arrow) in distal part of the left main bronchus; (B4) is the bronchoscopic image of MPP6, which shows the erosion of mucosa and secretions in the bronchus; (B5) is the bronchoscopic image of MPP4, which shows sputum plugging; (B6) is the bronchoscopic image of MPP3, the red arrow shows the proliferation of fibrous tissue occluded the bronchus orifice completely.