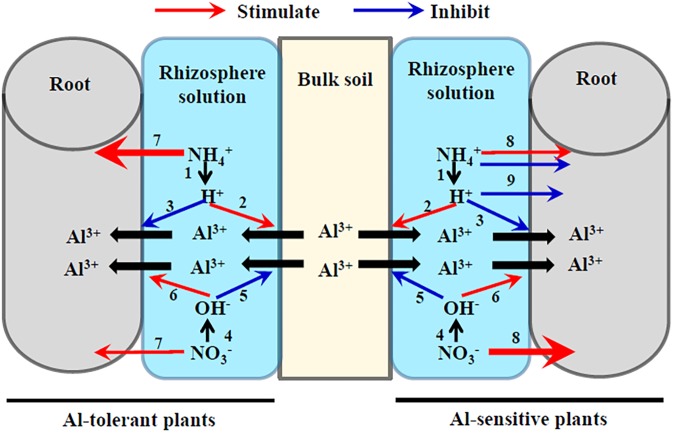
FIGURE 1.
Schematic diagram of possible effects of NH4+ and NO3- on the adsorption and desorption of Al on the root–soil interface. NH4+ acidifies rhizosphere solution (1), which stimulates the desorption of Al from bulk soils into rhizosphere solution (2) but inhibits the adsorption of Al from rhizosphere solutions to plant roots (3) both because of the competition between Al3+ and H+. In contrast, NO3- alkalizes rhizosphere solution (4), which inhibits the desorption of Al from soils into rhizosphere solution (5) but stimulates the adsorption of Al from rhizosphere solutions to plant roots (6) because NO3--increased negative electrical charge of root surface. Al-tolerant plant species prefer NH4+ to NO3- (7), while Al-sensitive plant species prefer NO3- to NH4+ (8). Excess NH4+ and H+ are both toxic to the growth of Al-sensitive plant species (9). Consequently, NH4+ alleviates Al toxicity to Al-tolerant plant species while aggravates Al toxicity to Al-sensitive plant species compared with NO3-.