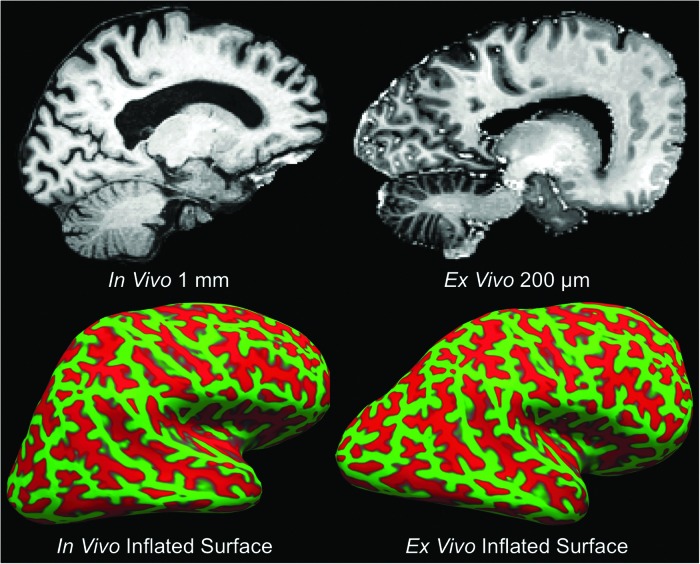
FIG. 7.
Co-registration of ex vivo and in vivo magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) data. Precise anatomic alignment of in vivo and ex vivo MRI datasets from an individual patient is challenging because postmortem fixation causes nonlinear deformations. A deformation is seen by comparing a sagittal image from the in vivo T1 multi-echo Magnetization Prepared Rapid Acquisition Gradient Echo dataset (top left) with a sagittal image from the ex vivo multi-echo flash dataset (top right). We developed a combined volume- and surface-based co-registration technique to address this challenge and obtain precise voxel-to-voxel match between the in vivo and ex vivo datasets. The inflated cortical surfaces generated from the in vivo and ex vivo datasets are shown in the bottom left and bottom right panels, respectively. Given that the topology of the cortical folds is invariant, this topology can be used to initialize a biomechanical nonlinear deformation. Color image is available online at www.liebertpub.com/neu